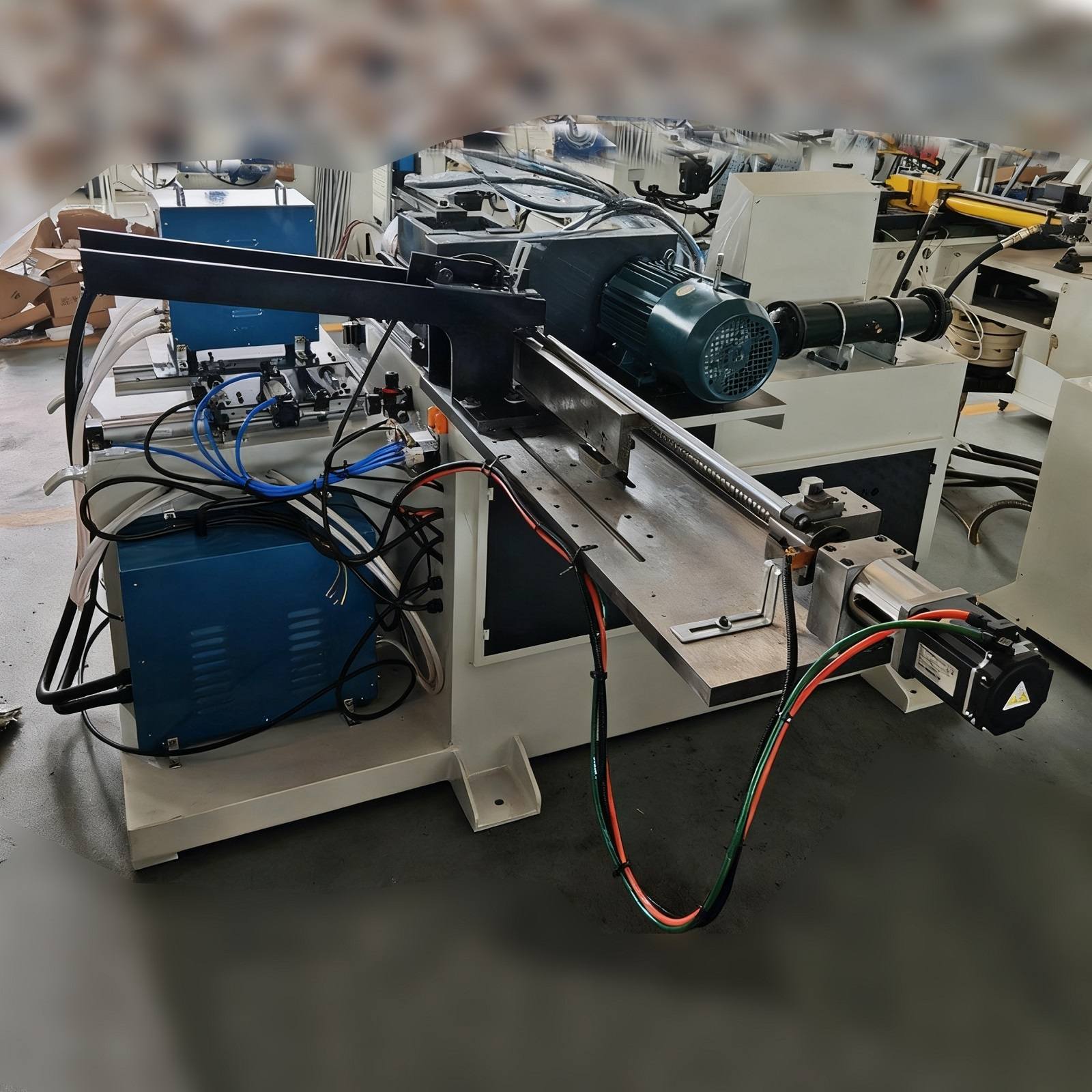
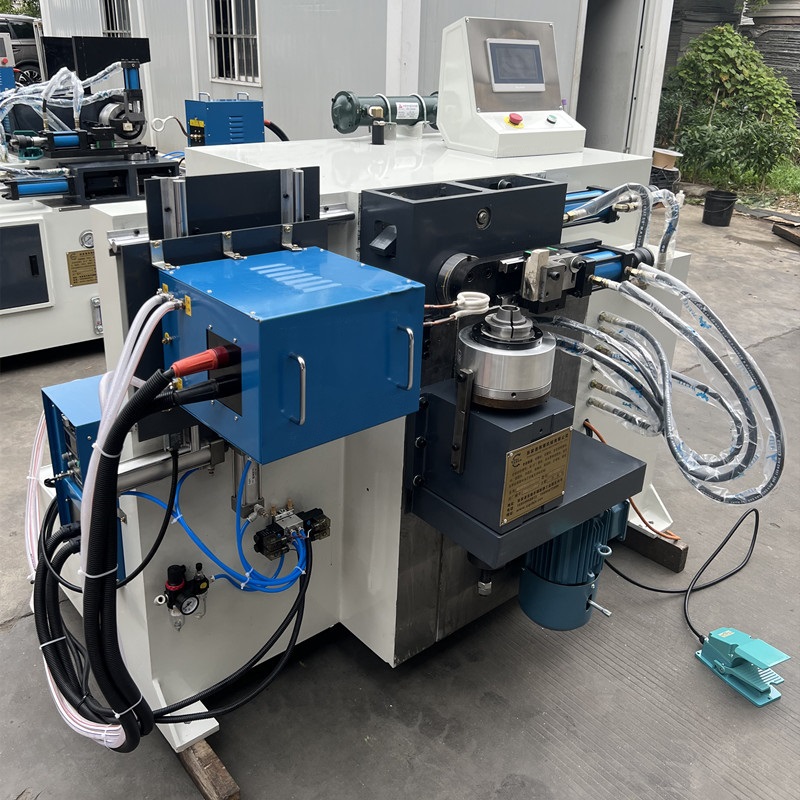
- 1.0Working Principle and Key Processes of the Tube End Closing Machine
- 2.0Key Differences Between the Tube End Closing Machine and Similar Equipment
- 3.0Main Machine Types and Technical Parameters of the Tube End Closing Machine
- 4.0How to Select a Tube End Closing Machine
- 5.0Operation and Maintenance Guidelines for the Tube End Closing Machine
- 6.0Frequently Asked Questions About Tube End Closing Machines
0.1Core Definition
A Tube End Closing Machine (also known as a tube end forming and closing machine) is a specialized industrial device that performs precise closing and forming operations on the ends of metal or non-metal tubes through processes such as mechanical pressing, hydraulic driving, thermal bonding, or rotary forming.
Its primary function is to shape tube ends into predefined closed-end structures—including necking, expanding, flanging, flat-end closing, and spherical-end closing—ensuring that the tube components achieve leak-free performance, protection against foreign matter intrusion, sufficient connection strength, and dimensional accuracy during subsequent assembly, pressure-bearing, and media transmission operations.
0.2Key Industrial Problems Solved
In industrial tube processing, improperly closed tube ends can lead to three critical issues:
- Pipeline leakage, resulting in the loss of essential media such as hydraulic oil, fuel, or refrigerants, which negatively affects downstream equipment operation;
- Foreign particle ingress into the tube interior, causing wear, blockage, or damage to precision components such as valves and pumps, thereby increasing maintenance costs;
- Insufficient structural stability at the tube end, failing to meet dimensional accuracy and strength requirements for subsequent assembly processes.
By integrating precise forming and closing operations into a single process, the Tube End Closing Machine effectively addresses these issues at the source, while simultaneously improving production efficiency, product consistency, and reducing manual operation errors.
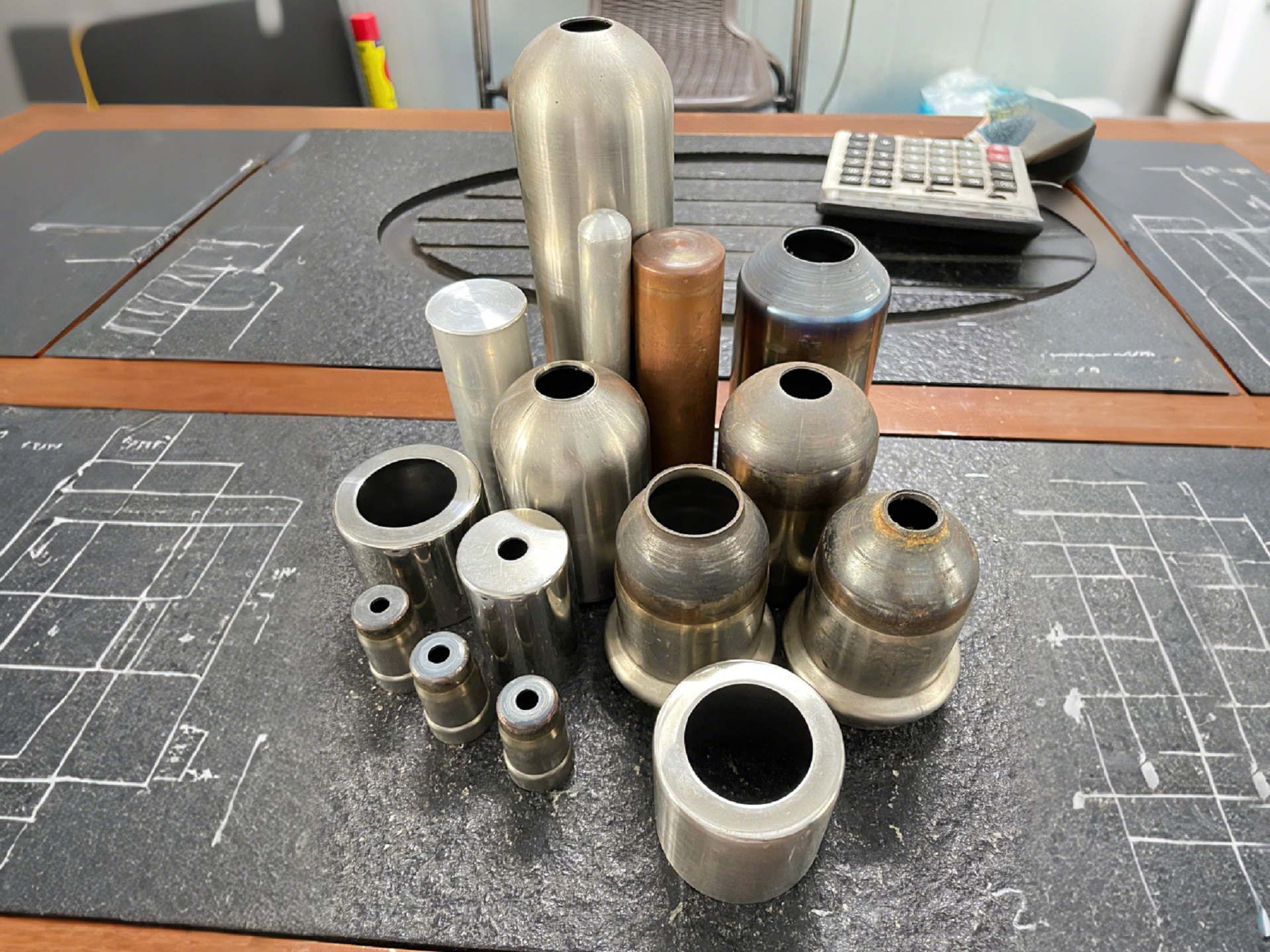

0.3Typical Industry Applications
The Tube End Closing Machine is widely used across multiple core industrial sectors, including but not limited to:
- Automotive Manufacturing: End closing of fuel pipes, brake lines, and air-conditioning pipelines to ensure driving safety and system reliability;
- Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems: Closing of high-pressure hydraulic tubes and pneumatic pipelines to meet strict leak-free connection requirements;
- Home Appliances & Refrigeration: End forming and closing of air-conditioning copper tubes and refrigerator aluminum tubes to maintain system vacuum integrity and sealing performance;
- Medical Devices: Precision processing of infusion tubes and medical gas delivery pipes, meeting high standards for biocompatibility and sealing accuracy;
- Construction & Engineering Machinery: Tube end closing of hydraulic pipelines used in mining machinery and excavators, suitable for high-strength sealing under harsh operating conditions.
0.4Processable Product Types
The Tube End Closing Machine is capable of processing a wide range of tube products, including:
- Sealing-Type Tube Components: Flat-closed tube ends, necked sealing tubes, expanded sealing tubes, flanged sealing tubes, and spherical-end closed tubes;
- Assembly-Type Tube Components: Tube ends designed for ferrule connections, flange connections, and threaded connections;
- Special-Function Tube Components: Bellows end closing, bulging and closing of thick-walled tubes, and complex curved-surface tube end forming (customized machine models required).
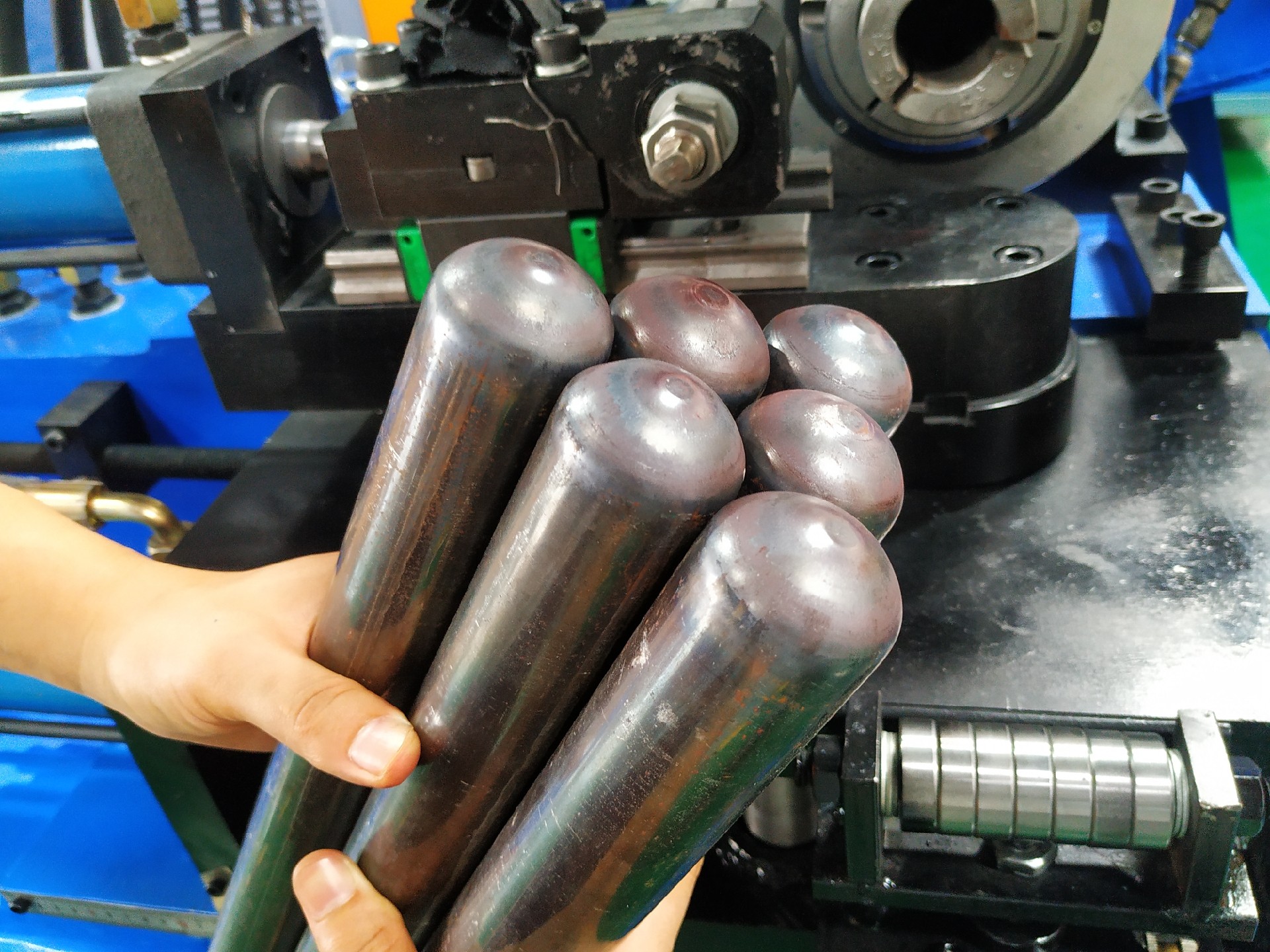

1.0Working Principle and Key Processes of the Tube End Closing Machine
1.1Basic Working Principle
The core working concept of a Tube End Closing Machine is based on the principle of constraint + energy input + forming solidification.
The tube end is precisely constrained by dedicated tooling, while controlled energy—such as mechanical force, hydraulic power, or thermal energy—is applied to induce plastic deformation or melting and solidification at the tube end.
As a result, the tube end is formed into a closed structure that exactly matches the mold cavity. By precisely controlling energy magnitude, application time, and tooling accuracy, consistent closing quality and dimensional stability are ensured.
1.2Core Driving Methods and Application Scenarios
Different driving systems are used in Tube End Closing Machines to suit various materials and processing requirements:
- Hydraulic Drive: Powered by high-pressure hydraulic cylinders, offering high energy output and stable pressure (typically 240–600 bar). This method is well suited for hard tubes and thick-walled tubes.
- Electric Drive: Utilizing servo motors combined with ball screw transmission, providing high precision (up to ±0.005 mm) and fast response. Ideal for small-diameter and high-precision tube processing.
- Pneumatic Drive: Driven by compressed air, featuring compact structure and low cost (operating pressure 0.6–0.8 MPa). Commonly used for thin-walled tubes and non-metallic tubes.
- Thermal Drive: Employing high-frequency induction heating or heating plates to melt the tube end. Suitable for non-metallic tubes or special metal tubes such as titanium alloys.
1.3Key Processes and Material Compatibility Requirements
Different tube materials require dedicated processes. Improper matching may lead to defects, as outlined below:
| Material / Product Type | Special Process Requirements | Defects to Avoid |
| Titanium alloy tubes | Hot rotary forming with heating at 800–1000°C and progressive feeding | Cracking, incomplete forming |
| Thin-walled stainless steel tubes | Soft clamping fixtures, reduced clamping force, low-speed pressing | Deformation, wrinkling |
| Medical plastic tubes | Ultrasonic closing with controlled frequency and pressure | Poor closing, odor generation |
| High-pressure hydraulic tubes | 24° cone sealing, pressure holding ≥ 8 seconds, subsequent pressure testing | Leakage, insufficient pressure resistance |
1.4Precision Control Methods
Precision control is the core guarantee of closing quality in a Tube End Closing Machine. Main control methods include:
- Servo closed-loop control, enabling real-time feedback and adjustment with accuracy up to ±0.005 mm;
- Pressure closed-loop control, preventing defects caused by overpressure or insufficient pressure;
- High-precision tooling, with mold tolerances controlled within ≤ 0.005 mm;
- Dedicated temperature PID control for thermal processes, ensuring dimensional consistency and stable forming results.
2.0Key Differences Between the Tube End Closing Machine and Similar Equipment
In industrial processing, the Tube End Closing Machine is often confused with tube-forming machines or chamfering machines. The essential differences are outlined below:
| Equipment Type | Core Function | Primary Objective | Typical Processes |
| Tube End Closing Machine | Integrated end forming and closing | Ensure sealing performance and prevent media leakage | Hydraulic pressing, thermal closing, rotary end closing |
| Tube Forming Machine | End shape forming only (no closing) | Meet assembly dimensional requirements | Expanding, reducing, non-sealing flanging |
| Tube End Chamfering Machine | Burr removal and chamfering | Improve end-face flatness and finish | Internal/external chamfering, end-face trimming |
| Welding Machine | Tube joining or end-cap welding | Achieve connection or permanent closure | TIG welding, plasma welding |
3.0Main Machine Types and Technical Parameters of the Tube End Closing Machine
3.1Classification by Driving Method and Key Parameters
Different Tube End Closing Machine models can be categorized according to their driving systems. Typical parameters and application scenarios are shown below:
| Drive Type | Applicable Tube Diameter | Working Pressure | Forming Accuracy | Suitable Materials | Typical Applications |
| Hydraulic Drive | Ø6–Ø80 mm (customized up to Ø600 mm) | 240–600 bar | ±0.02–±0.05 mm | Hard metal tubes, thick-walled tubes | Construction machinery, high-pressure hydraulic pipes |
| Electric Drive | Ø3–Ø20 mm | Adjustable as required | ±0.005–±0.01 mm | Precision metal tubes, small plastic tubes | Medical devices, aerospace |
| Pneumatic Drive | Ø3–Ø50 mm | 0.6–0.8 MPa | ±0.02–±0.05 mm | Thin-walled tubes, non-metal tubes | Home appliances, refrigeration, light-duty tubing |
| Thermal Drive | Ø3–Ø50 mm | Adjustable as required | ±0.02–±0.05 mm | Plastics, titanium alloys | Medical plastic tubes, special metal tubes |
3.2Classification by Automation Level
Based on production scale and automation requirements, Tube End Closing Machines can be divided into the following types:
- Manual Models
Manual loading and clamping, suitable for small-batch trial production.
Typical cycle time: 10–20 seconds per piece.
Hourly output: approximately 180–360 pieces. - Semi-Automatic Models
Manual loading with automatic processing and unloading, suitable for small- to medium-batch production.
Typical cycle time: 5–10 seconds per piece.
Hourly output: approximately 360–720 pieces. - Fully Automatic Models
Automatic feeding, inspection, and sorting, suitable for large-scale standardized production.
Typical cycle time: 2–5 seconds per piece.
Hourly output: approximately 720–1,800 pieces.
4.0How to Select a Tube End Closing Machine
4.1Core Selection Criteria
When selecting a Tube End Closing Machine, the following factors should be clearly defined in advance:
- Product requirements: Tube diameter, wall thickness, end-closing structure, and accuracy requirements, which form the fundamental basis for selection;
- Material characteristics: Hydraulic or electric models are recommended for hard metal tubes, while thermal or pneumatic models are more suitable for non-metal tubes;
- Production volume: Manual or semi-automatic models with fast mold change are suitable for small batches and multiple product types, while fully automatic multi-station models are preferred for large-scale production.
4.2Key Parameter Matching Principles
Proper parameter matching is critical to ensure the stable performance of a Tube End Closing Machine:
- Tube diameter matching: The machine’s processing range should fully cover the required tube diameter, with a recommended allowance of 5–10 mm;
- Pressure matching: Hard or thick-walled tubes typically require 400–600 bar, while thin-walled or non-metal tubes require 0.6–0.8 MPa or 240–300 bar;
- Accuracy matching: General industrial applications usually require ±0.02–±0.05 mm, while precision products for aerospace or medical applications require ±0.005–±0.01 mm;
- Capacity matching: The machine’s hourly output should exceed actual production demand by 10–20% to accommodate maintenance and mold change time.
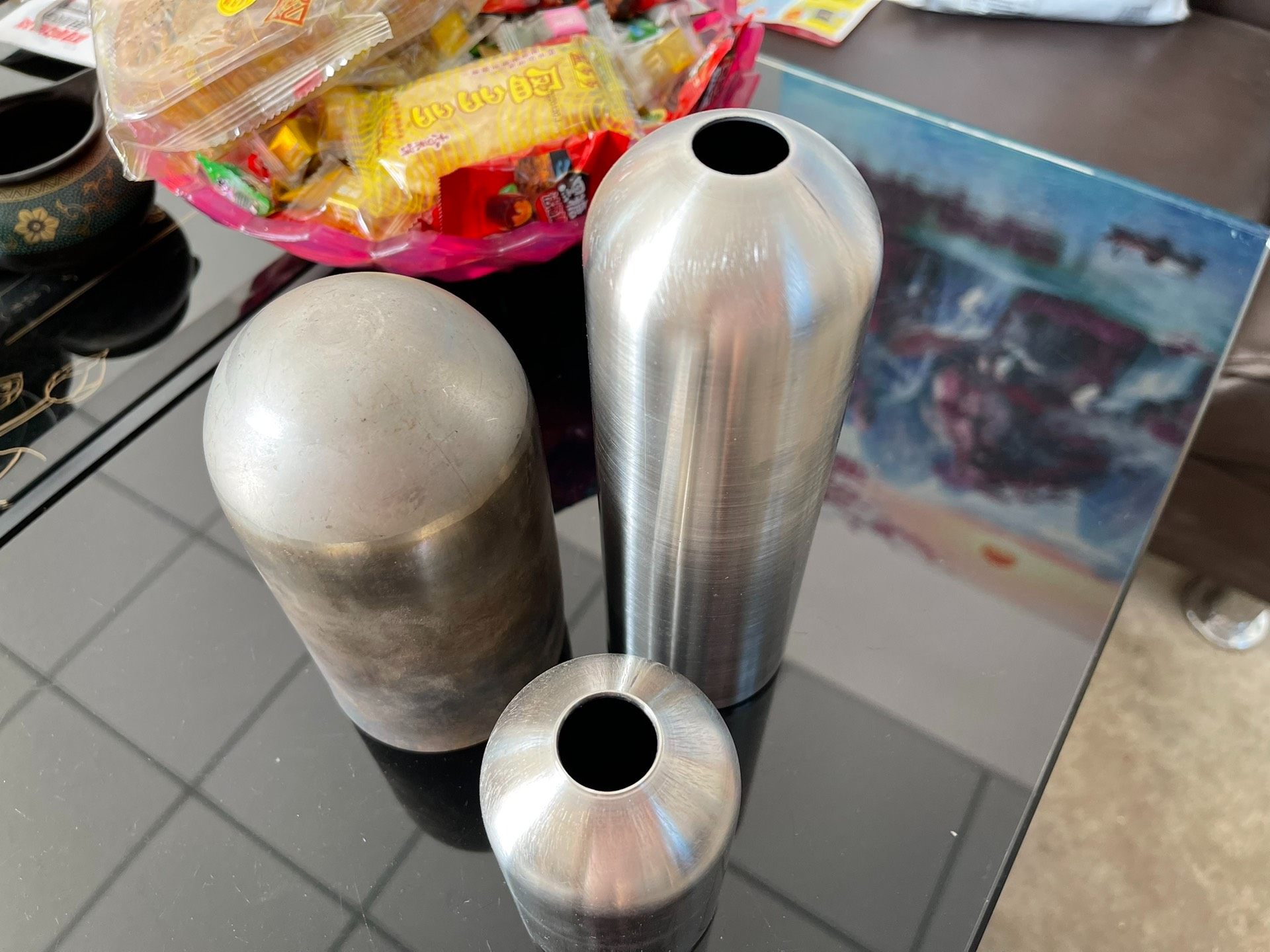


4.3Common Selection Mistakes to Avoid
The following common mistakes should be avoided when selecting a Tube End Closing Machine:
- Blindly pursuing ultra-high precision for standard household appliance tubes, which unnecessarily increases procurement costs;
- Ignoring material compatibility, such as using hydraulic machines for thin-walled plastic tubes that may deform easily, or pneumatic machines for thick-walled stainless steel tubes that may result in incomplete forming;
- Underestimating production capacity requirements by failing to consider mold changes and maintenance downtime, leading to unmet output targets;
- Overlooking future expansion needs, such as choosing manual models without upgrade potential for small-batch production, resulting in the need for complete replacement during capacity expansion.
4.4Recommended Optional Configurations
Depending on production requirements, the following configurations can be selected for a Tube End Closing Machine:
- Quick mold change system, enabling mold replacement within 1–2 minutes for multi-product applications;
- Automatic loading and unloading, significantly improving productivity and automation levels;
- In-line inspection, integrating dimensional and sealing performance checks to automatically reject defective products;
- Data connectivity, supporting smart factory systems for production monitoring and remote maintenance.
5.0Operation and Maintenance Guidelines for the Tube End Closing Machine
5.1Basic Operating Procedure (Simplified)
A typical operating process for a Tube End Closing Machine includes the following steps:
- Startup inspection, ensuring hydraulic oil, air pressure, tooling, and safety devices are in proper condition;
- Parameter setup, adjusting pressure, stroke, and holding time according to tube specifications;
- Trial processing, producing one to three test pieces to verify dimensions and closing performance;
- Formal production, carrying out batch processing with automatic operation and periodic sampling inspection;
- Shutdown and cleaning, turning off power and air supply, and cleaning molds and residual materials.
6.0Frequently Asked Questions About Tube End Closing Machines
What is a Tube End Closing Machine?
A Tube End Closing Machine is an industrial machine designed to close and form the ends of metal or non-metal tubes through mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic, or thermal processes. It creates leak-proof tube ends to prevent media leakage and foreign matter ingress in pipelines and assemblies.
What is a Tube End Closing Machine used for?
A Tube End Closing Machine is used to seal or close tube ends in applications such as automotive fuel lines, hydraulic pipes, refrigeration tubes, medical tubing, and construction machinery pipelines, ensuring reliable sealing and structural strength.
What materials can a Tube End Closing Machine process?
A Tube End Closing Machine can process a wide range of materials, including aluminum tubes, stainless steel tubes, copper tubes, titanium alloy tubes, plastic tubes, and composite tubes, depending on the selected drive method and tooling.
What is the difference between a Tube End Closing Machine and a Tube Forming Machine?
A Tube End Closing Machine integrates both end forming and sealing functions to ensure leak-proof performance, while a Tube Forming Machine only shapes the tube end without sealing and is mainly used to meet assembly dimensional requirements.
What is the difference between a Tube End Closing Machine and a Tube End Sealing Machine?
In many markets, Tube End Closing Machine and Tube End Sealing Machine are used interchangeably. However, Tube End Closing Machine is often preferred when describing mechanical end-closing, crimping, or forming processes, especially for metal tubes.
Which drive type is best for a Tube End Closing Machine?
The best drive type for a Tube End Closing Machine depends on the application:
- Hydraulic drive for hard or thick-walled metal tubes
- Electric drive for high-precision small-diameter tubes
- Pneumatic drive for thin-walled or non-metal tubes
- Thermal drive for plastic tubes or special alloys such as titanium
What tube diameter range can a Tube End Closing Machine handle?
Standard Tube End Closing Machines typically process tube diameters from Ø3 mm to Ø80 mm, while customized machines can handle diameters up to Ø600 mm for large industrial applications.
How accurate is a Tube End Closing Machine?
The forming accuracy of a Tube End Closing Machine ranges from ±0.05 mm for general industrial use to ±0.005 mm for high-precision applications such as medical devices and aerospace components.
Is a Tube End Closing Machine suitable for high-pressure pipes?
Yes. A Tube End Closing Machine is widely used for high-pressure hydraulic pipes and fuel lines, provided that the correct pressure level, forming structure, and post-processing pressure testing are applied.
Can a Tube End Closing Machine be fully automatic?
Yes. A Tube End Closing Machine can be configured as a manual, semi-automatic, or fully automatic system with automatic feeding, unloading, inspection, and sorting for large-scale production.
How do I choose the right Tube End Closing Machine?
To choose the right Tube End Closing Machine, consider tube diameter, wall thickness, material type, required sealing structure, accuracy requirements, and production capacity. Matching these parameters is critical for stable and cost-effective operation.