- 1.0What Is a Press Machine and How Does It Work?
- 2.0Types of Press Machines: Classification Overview
- 3.0Manual Fly Press: Simple and Reliable Metal Forming Tool
- 4.0Power Press: High-Speed Solution for Mass Production
- 5.0Frame Designs of Press Machines
- 6.0Press Working: Cold Stamping Processes in Sheet Metal
- 7.0Die Materials Used in Press Tools
- 8.0Conclusion: Choosing the Right Press Machine for Your Industry
Press machines are essential tools in sheet metal fabrication, used across a wide range of industries, including automotive manufacturing, appliance production, HVAC systems, and aerospace component fabrication. These machines allow manufacturers to form or cut metal using high-pressure force, shaping metal into desired parts with extreme precision and efficiency.
Whether you’re working with a mechanical press, hydraulic press, or fly press, understanding their types, structures, operations, and die materials is critical for any production environment. This blog walks you through everything you need to know about press machines.
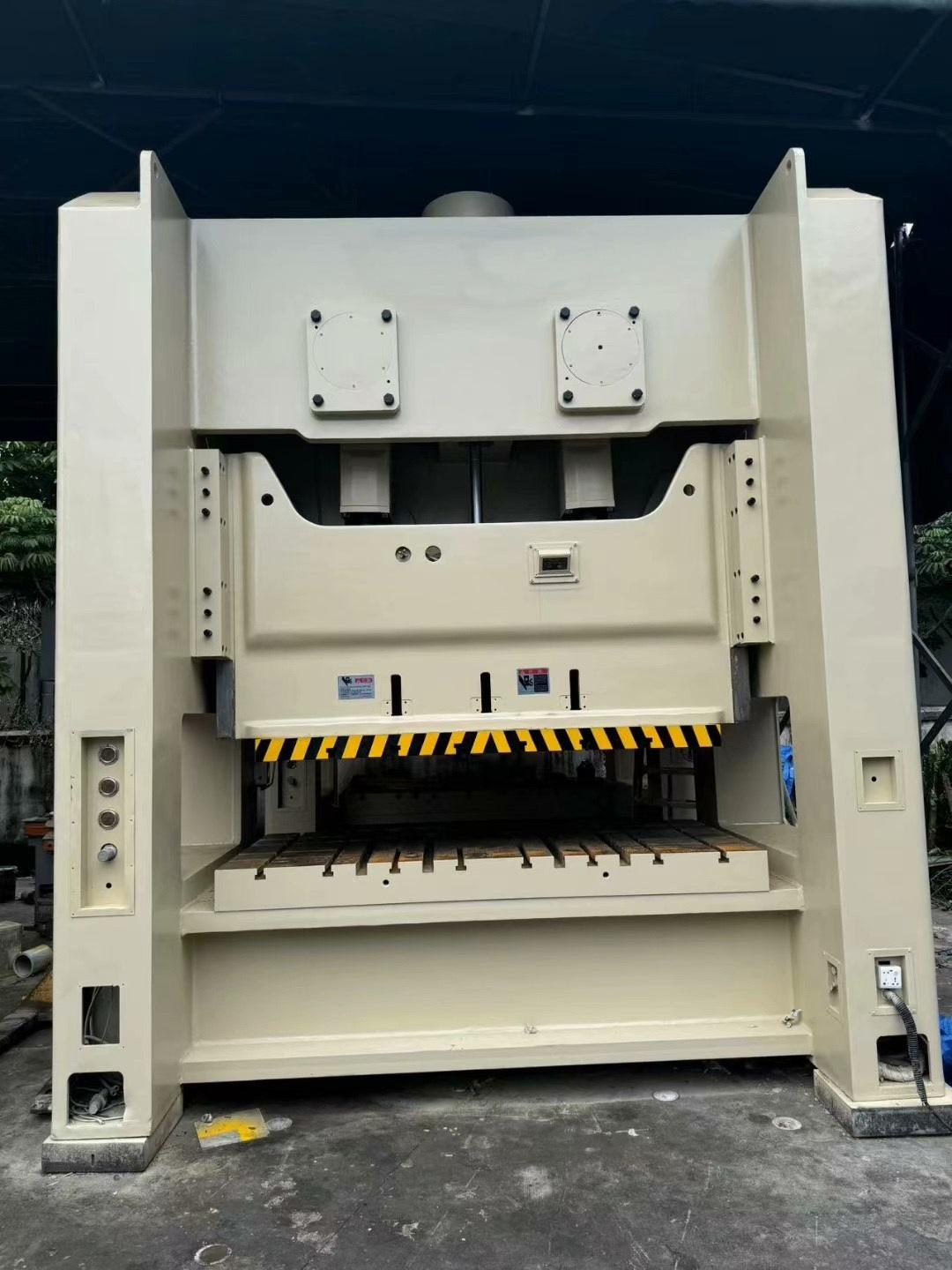
1.0What Is a Press Machine and How Does It Work?
A press machine is a metal forming tool designed to cut or shape sheet metal without removing chips. It operates by applying mechanical or hydraulic force to a punch and die set, producing parts with high accuracy and repeatability.
Key industries using press machines include:
- Automotive stamping (e.g., fenders, brackets, frames)
- Home appliances (e.g., metal enclosures, washer drums)
- Aerospace sheet metal components
- Electrical enclosures and HVAC ductwork
The main advantage of using a press machine is its ability to mass-produce sheet metal components efficiently, making it indispensable in high-volume manufacturing.
2.0Types of Press Machines: Classification Overview
Press machines can be classified based on power source and frame design:
2.1Classification by Power Source
- Manual Press (Fly Press / Ball Press)
- Power Press (Mechanical or Hydraulic)
2.2Classification by Frame Design
- Gap Frame Press
- Inclined Frame Press
- Adjustable Bed Press
- Horn Press
- Straight Side Press
- Pillar Press
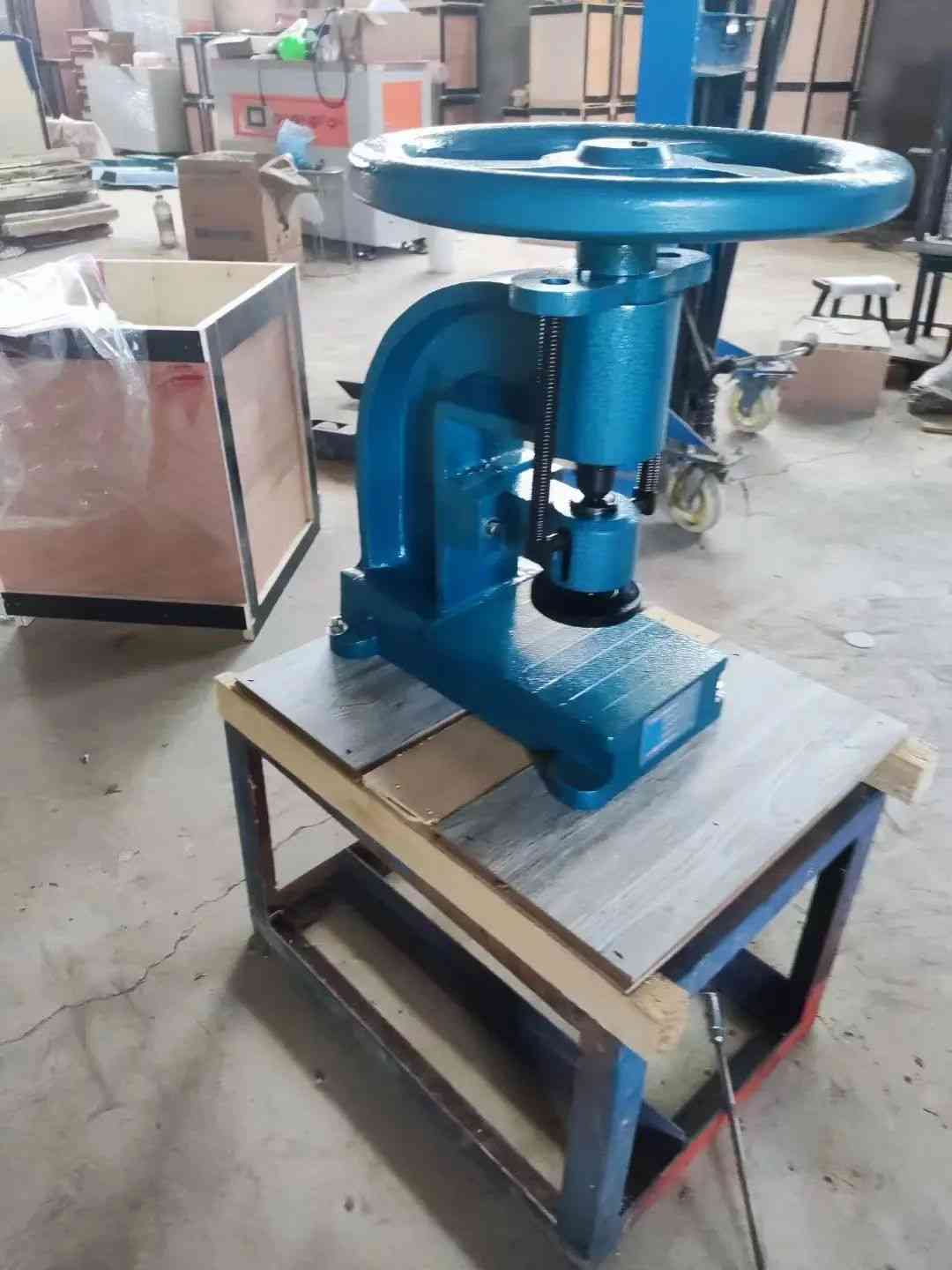
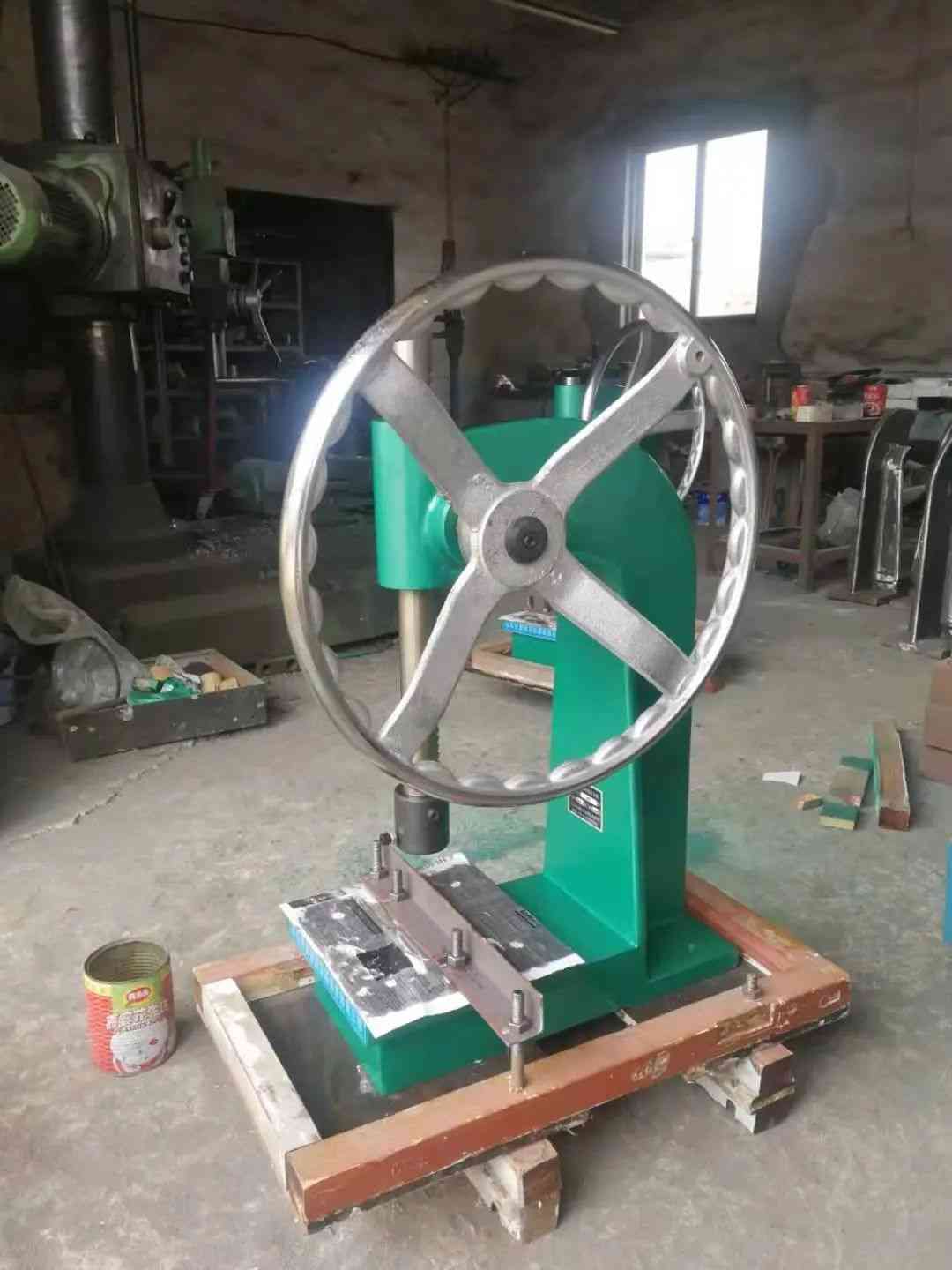
3.0Manual Fly Press: Simple and Reliable Metal Forming Tool
The fly press (also called hand press or ball press) is a manually operated metal punching machine, ideal for prototype work, small-batch forming, and simple hole punching.
The typical structure of a fly press includes:
- Rigid C-frame
- Ram, screw, iron balls, and rotating handle
- Punch and die mounted on a bolster plate
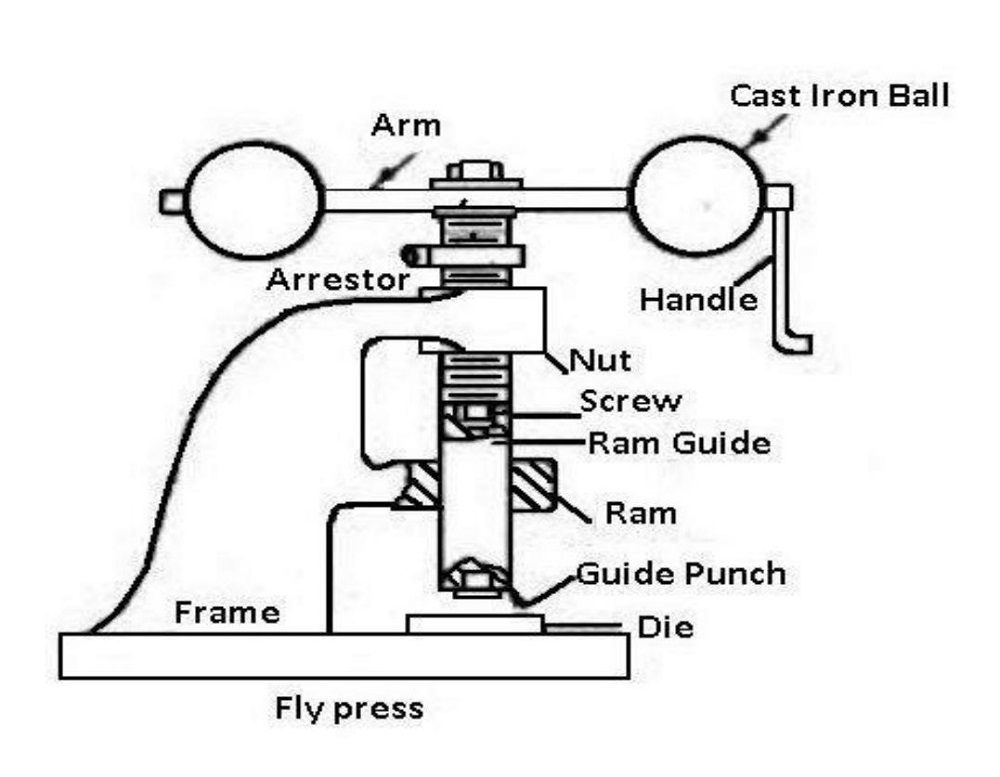
The operation relies on rotating a handle that transfers kinetic energy via iron balls to drive the ram downward. It’s commonly used for custom metal parts, jewelry stamping, and small precision forming.


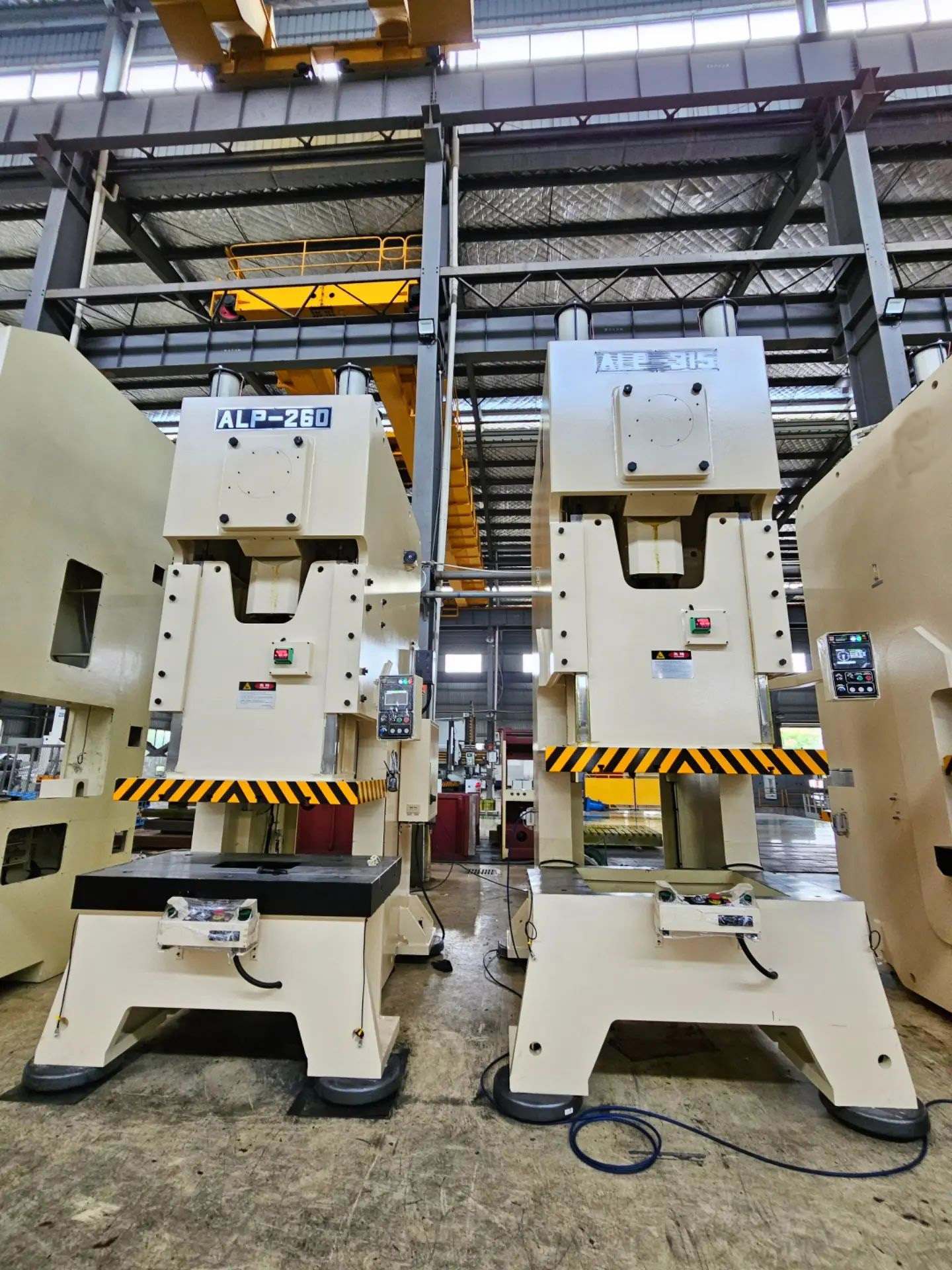
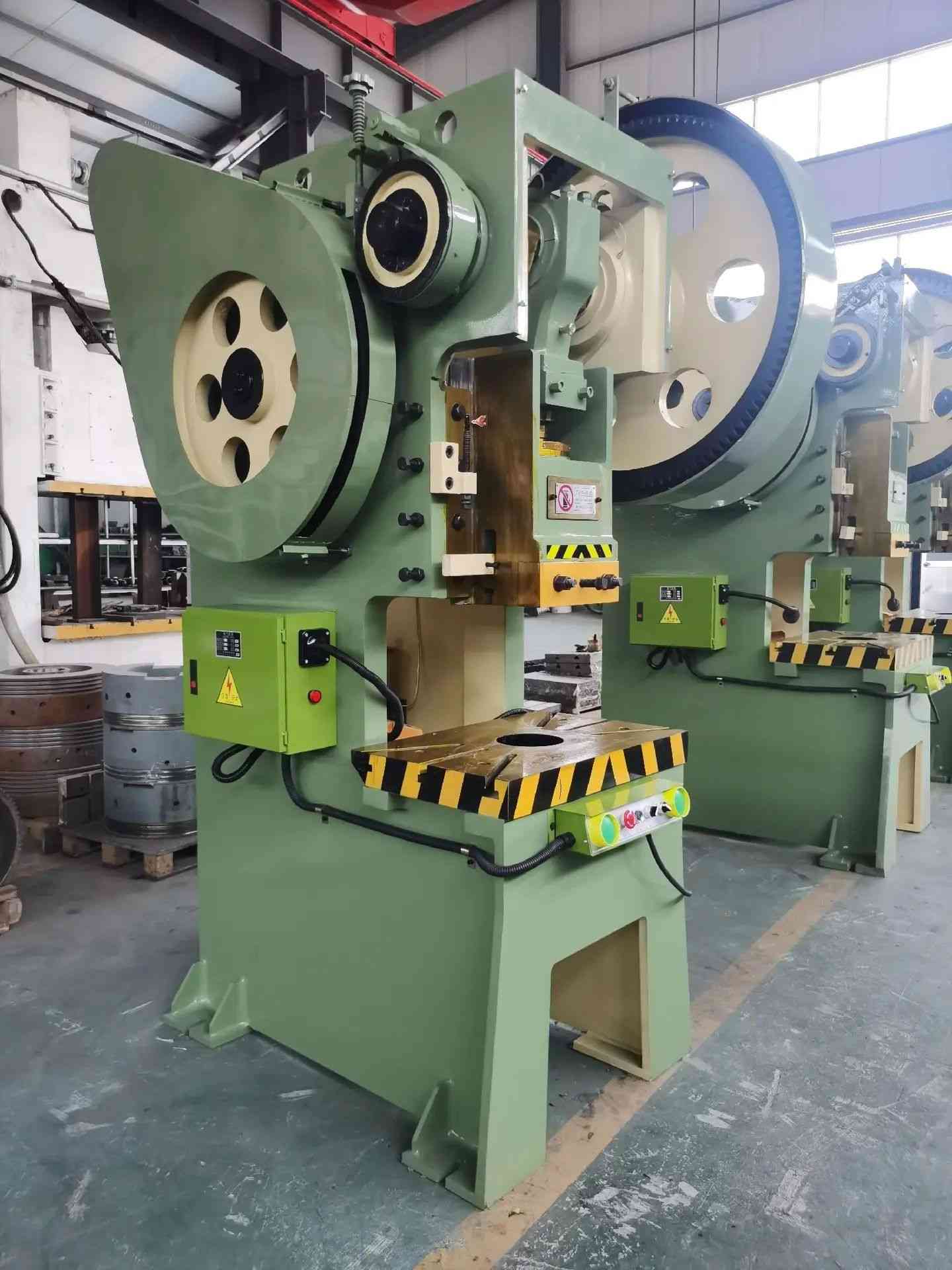
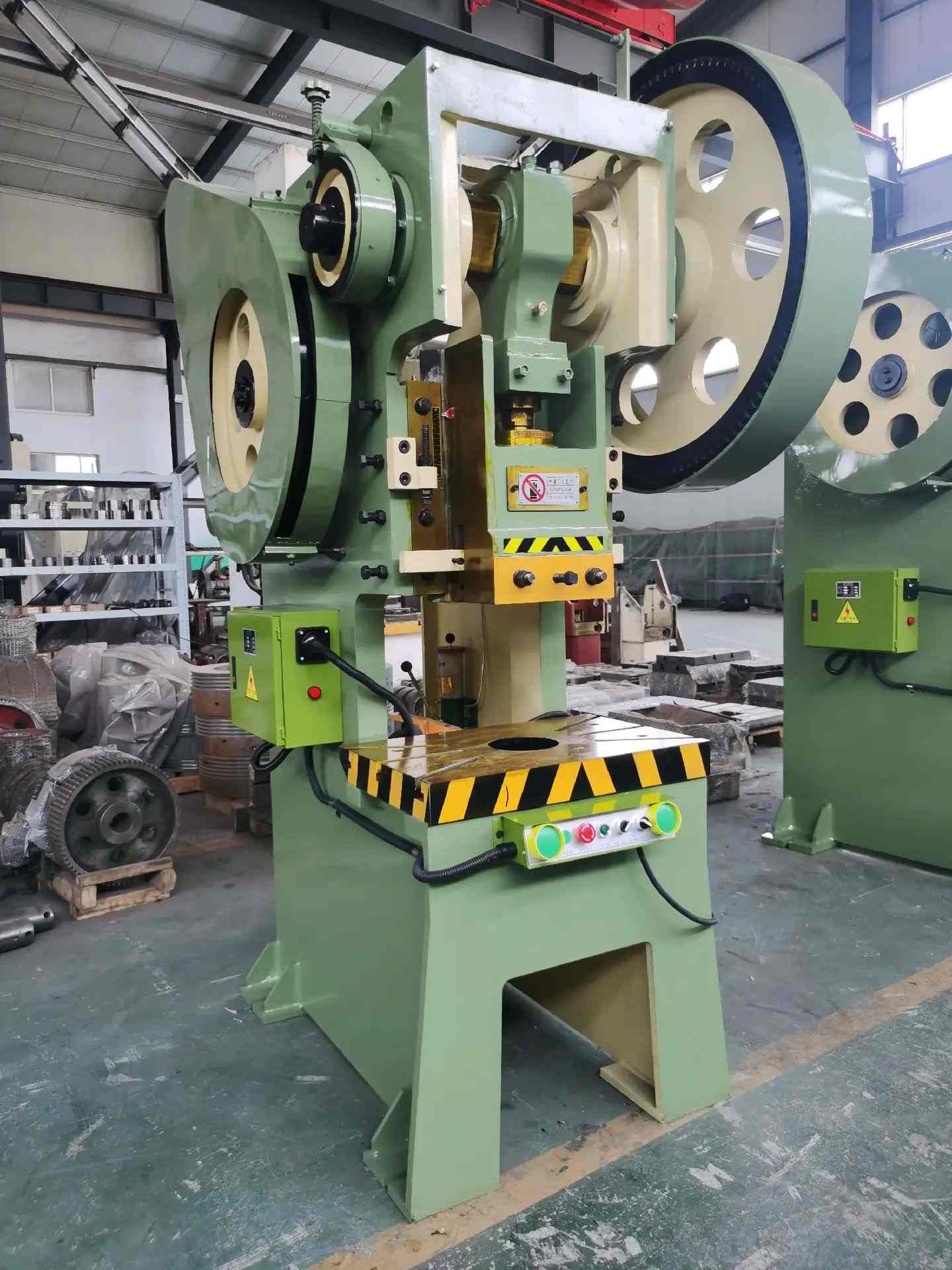
4.0Power Press: High-Speed Solution for Mass Production
The power press machine is the most widely used type in industrial environments. Instead of manual input, it uses mechanical or hydraulic power to drive the ram.
Types of power press machines:
- Mechanical Press: Crank and connecting rod mechanism, suitable for progressive die stamping and blanking.
- Hydraulic Press: Used for deep drawing, embossing, and large panel forming.
A flywheel stores energy and maintains consistent force throughout the downward stroke. These machines are commonly found in CNC punch press lines, press brake lines, and robotic sheet metal cells.
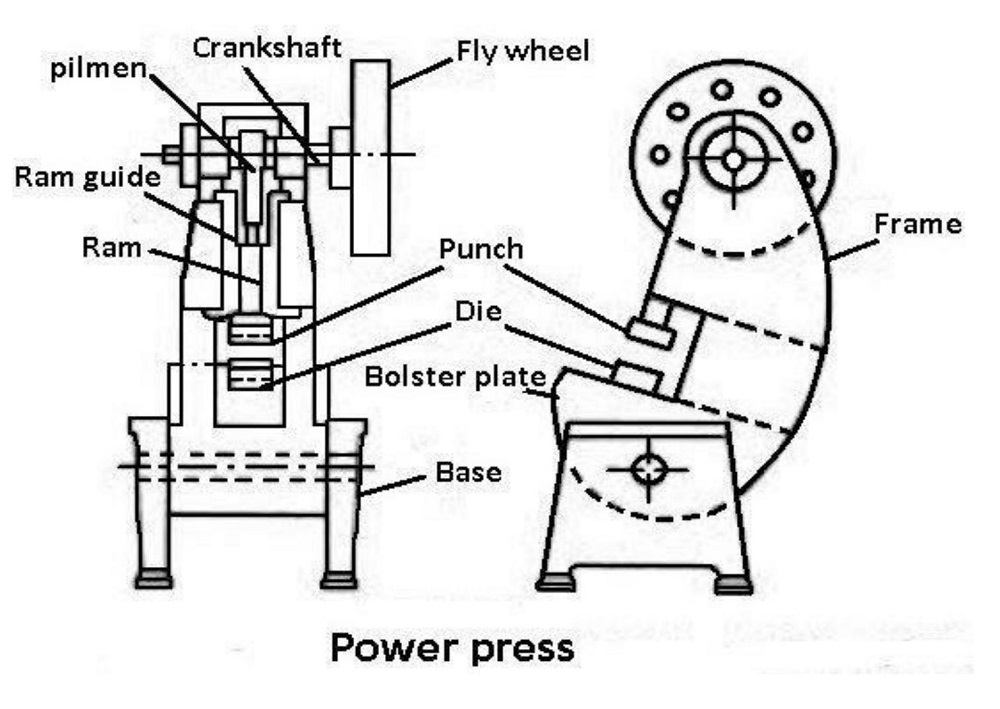


5.0Frame Designs of Press Machines
5.1Gap Frame Press
Features an open frame that provides easy access to the sides for sheet feeding. Suitable for general stamping and moderate load applications.
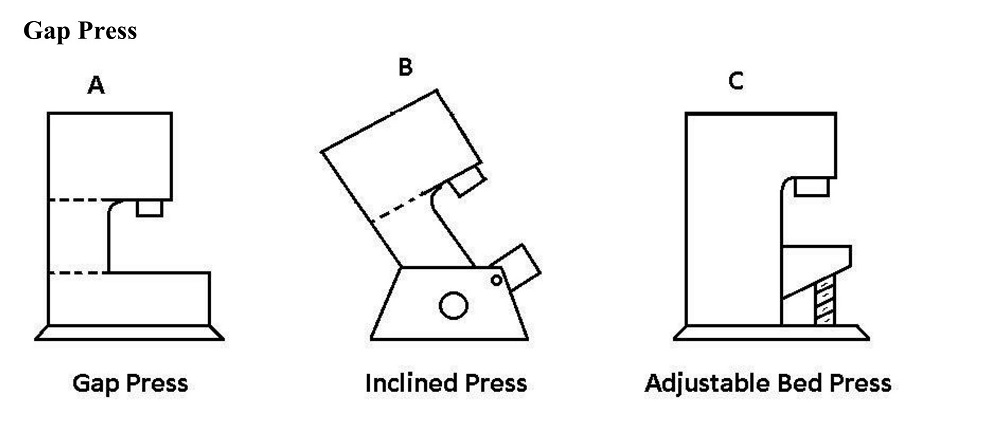
5.2Inclined Frame Press
Can tilt backward to discharge scrap and finished parts using gravity. Widely used in automated stamping lines.
5.3Adjustable Bed Press
Allows the worktable to raise or lower, accommodating different die heights. Ideal for tooling flexibility.
5.4Horn Press
Features a cylindrical horn extension to support cylindrical workpieces like pipes or tubes. Useful in pipe punching and round embossing.
5.5Straight Side Press
Has two rigid vertical frames that handle heavy loads, perfect for automotive panel forming or high-tonnage applications.
5.6Pillar Press
A hydraulic press design with four guiding pillars ensures high stability during high-precision operations.
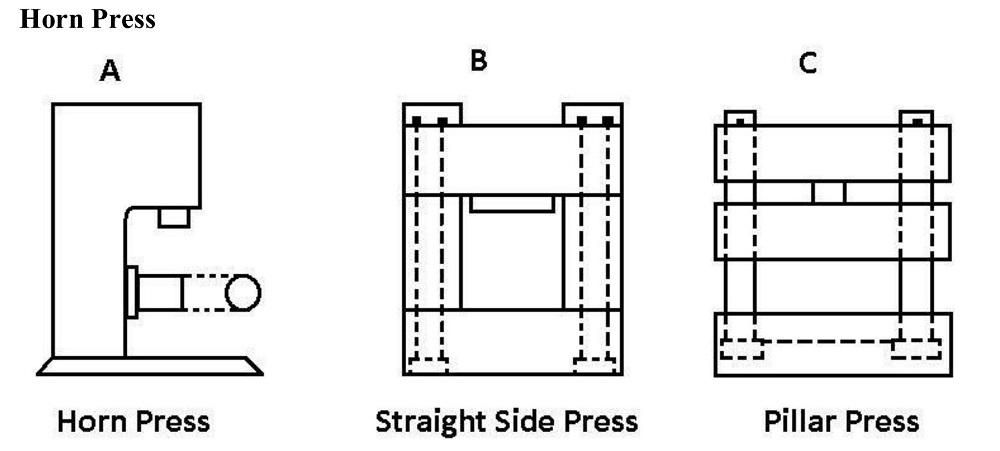
6.0Press Working: Cold Stamping Processes in Sheet Metal
Press working, also known as cold stamping, refers to the process of producing parts from sheet metal using a press machine. The two main categories are:
6.1Cutting Operations
These involve shear stress to cut through the metal:
- Blanking: Cutting flat shapes (the blank is the part).
- Punching: Creating holes (the slug is scrap).
- Notching: Cutting from the edge.
- Perforating: Producing closely spaced holes.
- Trimming: Removing excess material.
- Shaving: Refining edges for tight tolerances.
- Slitting: Partial cutting of material.
- Lancing: Partially cutting and bending to create tabs.
- Nibbling: Cutting complex shapes by successive punches (common in CNC turret punch systems).
6.2Forming Operations
These change the shape without removing material:
- Bending: Angular deformation.
- Drawing: Stretching into a cup-like shape.
- Squeezing: Compressing metal to form ribs or embossments.
These operations are widely used in HVAC duct forming, electrical cabinet production, and stainless steel kitchenware fabrication.
7.0Die Materials Used in Press Tools
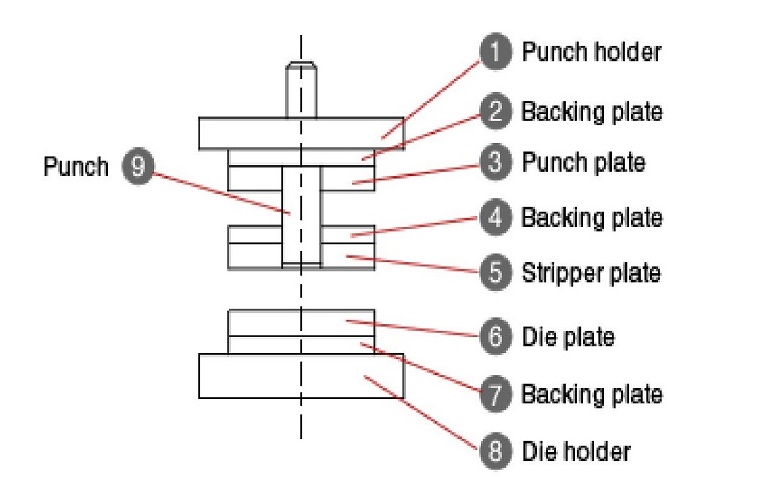
Die components must withstand repeated force and wear. Common die materials include:
- Die Holder
- Materials: SS400, S50C, FC250, SKS3, A7075
- Provides structural support and houses springs.
- Backing Plate
- Materials: SK3, SK5, SKS3, S50C
- Protects dies from over-penetration, supports stripper components.
- Punch Plate
- Materials: SS400, S50C, SKS3, SKD11
- Holds small punches in place.
- Stripper Plate
- Materials: S50C, SKS3, SKD11
- Removes scrap and guides the punch.
- Die Plate
- Materials: SKS3, SKD11
- Standard material for mass production dies using wire EDM cutting.
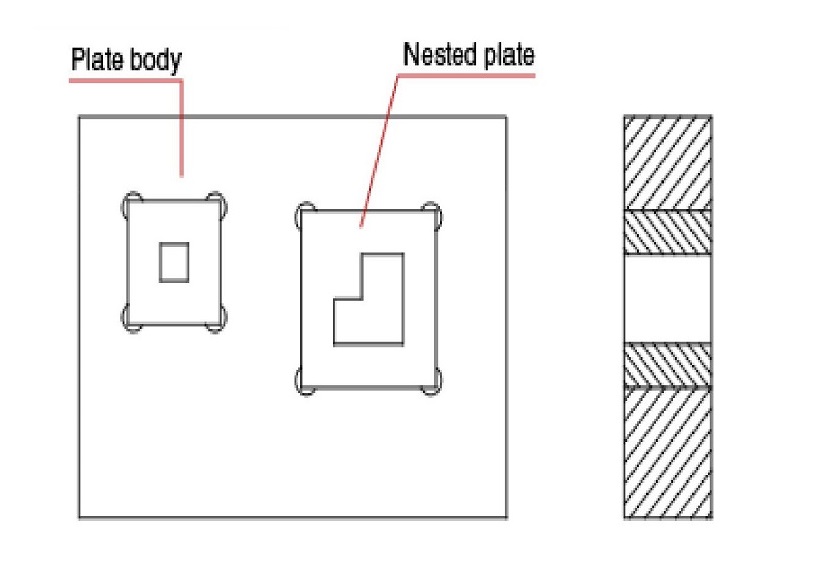
- Nested Plates
- Materials: S50C (low volume), SKD11, SKH51, Carbide (high volume)
- Allow easy maintenance and die changes.
- Punches
- Materials: SKD11, SKS3, SKH51, powdered HSS, carbide
- Carbide and powder steels are used for high-wear applications in automotive stamping lines.
8.0Conclusion: Choosing the Right Press Machine for Your Industry
Whether you’re producing automotive chassis parts, electrical enclosures, or custom HVAC panels, the right press machine—be it fly press, mechanical press, or hydraulic pillar press—will significantly impact your production speed, product quality, and cost efficiency.
By understanding press machine types, structures, working processes, and die materials, manufacturers can optimize tooling design, extend die life, and achieve consistent results in high-volume metal stamping operations.









