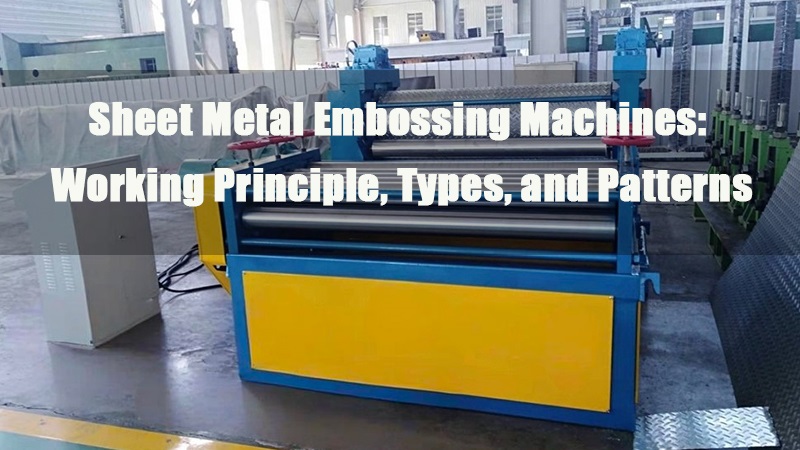
- 1.0What Is Metal Embossing?
- 2.0Process Principle of Metal Embossing
- 3.0What Is a Sheet Metal Embossing Machine?
- 4.0Types and Applications of Embossed Metal Sheets
- 5.0Configuration of a Sheet Metal Embossing Production Line
- 6.0Advantages and Applications of Metal Embossing
- 7.0Manufacturing Process of Diamond Plate
- 8.0How to Choose the Right Sheet Metal Embossing Machine
- 9.0Conclusion
- 10.0Metal Embossing FAQ
1.0What Is Metal Embossing?
Metal embossing is a manufacturing technique that uses high-pressure engraved rollers or dies to imprint patterns, textures, or lettering onto the surface of metal sheets. Unlike surface embossing on plastics or coated materials, this process alters the metal substrate’s surface profile through plastic deformation, creating textured features with measurable depth.
In modern manufacturing, sheet metal serves not only as a structural component but also plays a vital role in product aesthetics and functionality, key factors in overall market competitiveness. It is in this context that the Sheet Metal Embossing Machine has emerged.
Metal embossing is widely applied across architectural decoration, transportation, appliance panels, and industrial packaging. Whether the goal is to enhance slip resistance and durability or to improve product identity through surface design, the embossing process offers a solution that combines both form and function.

2.0Process Principle of Metal Embossing
Metal embossing is a cold forming process based on physical deformation, where pressure is applied directly to the metal substrate to create permanent raised and recessed patterns. Unlike decorative embossing,g that only forms textures on the surface layer of Plastisol coatings, metal embossing induces plastic deformation of the metal surface itself, significantly altering its texture and performance characteristics.
The process typically employs a pair of high-hardness engraved rollers (embossing rolls) to apply pressure to metal sheets or coils. This method enables precise pattern transfer without damaging any existing surface coatings, making it compatible with both pre-painted and post-painted metal materials.
The fundamental steps of the process are as follows:
- The metal sheet or coil is continuously fed between a pair of precision-engraved embossing rollers;
- Under synchronized pressure from the upper and lower rollers, the metal surface undergoes plastic flow, forming a three-dimensional texture that replicates the roller design.
- The rollers are usually configured in a male-female pair, enabling either symmetrical double-sided embossing or customized decorative effects.
- The entire process can be integrated into high-speed continuous production lines, making it ideal for industrial-scale manufacturing of standardized, high-volume products.
3.0What Is a Sheet Metal Embossing Machine?
Metal embossing machines can be categorized into several types based on their application and level of automation:
- Coil-to-Coil Embossing Machines: High-efficiency solution for continuous embossing of metal coils in automated lines.
- Sheet Embossing Machines: Used for embossing individual metal sheets, ideal for medium- to small-batch production and customized designs.
- Integrated Embossing Units: These units can be embedded into roll forming lines, slitting lines, or color coating lines, enabling flexible and modular production.
- Manual or Semi-Automatic Embossing Machines: Suitable for prototyping, small batch runs, or artistic metalworking applications.
Each machine can be configured according to the type of metal material, thickness, desired embossing depth, and production volume requirements.

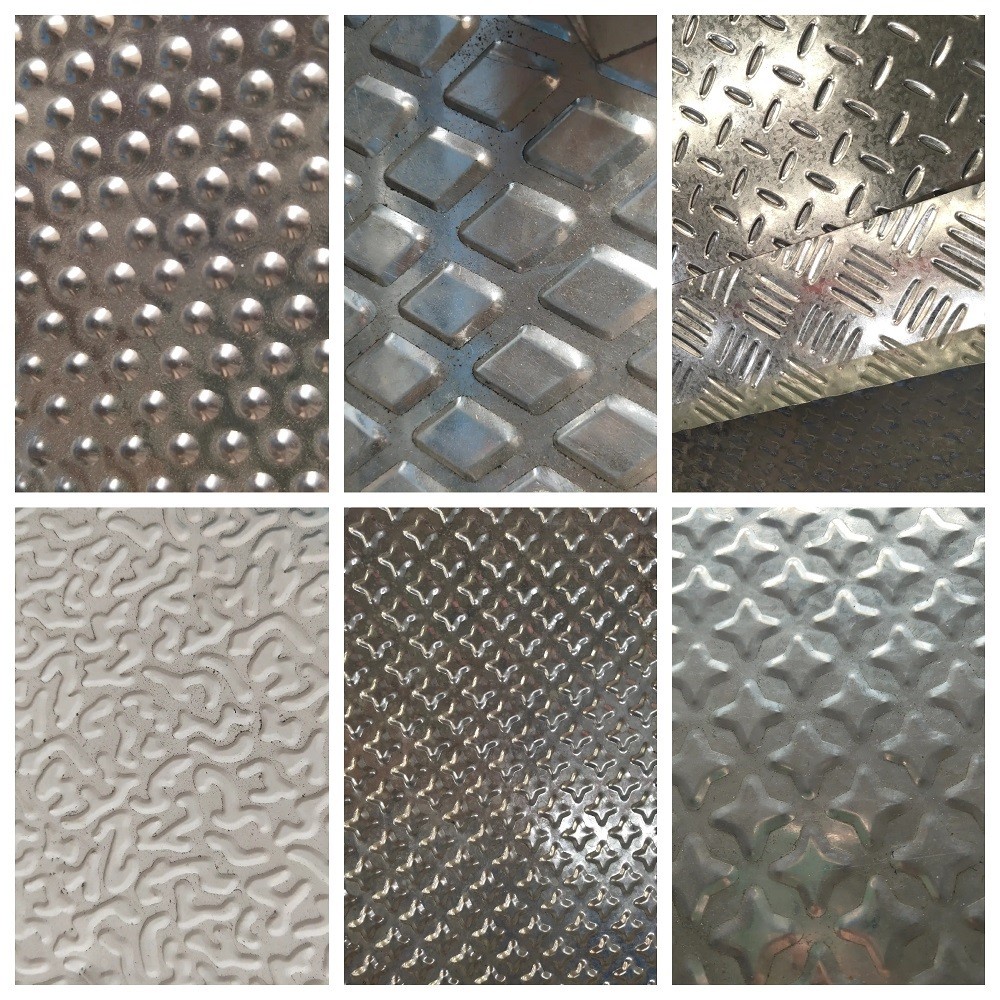
4.0Types and Applications of Embossed Metal Sheets
Embossed metal sheets vary in material, surface pattern, and performance characteristics, making them suitable for a wide range of industrial and decorative applications. Below are three common types of embossed sheets, along with typical product examples and application insights:
4.1Aluminum Embossed Plate
Common Patterns: Five Bar, Orange Peel, Diamond, Checker
Typical Products:
- Aluminum Checker Plate
- Aluminum Tread Plate
- Orange Peel Embossed Aluminum Sheet
- Stucco Embossed Aluminum Coil
- Diamond Pattern Aluminum Sheet
Applications:
Stair treads, truck flooring, cold storage wall panels, machinery housings, decorative cladding
Process Features:
Lightweight and easy to process; compatible with low- to medium-pressure embossing machines; excellent thermal conductivity; high cost-effectiveness
4.2Stainless Steel Embossed Sheet
Common Patterns: Water Ripple, Small Bead, Linen, Leather, Diamond
Typical Products:
- 304 Water Ripple Stainless Steel Sheet
- 201 Linen Pattern Stainless Steel Plate
- Anti-Slip Stainless Steel Diamond Plate
- Leather Finish Stainless Steel Panel
- Mirror Finish Bead Embossed Stainless Sheet
Applications:
Elevator doors, commercial building columns, kitchen anti-slip flooring, wall and ceiling decoration
Process Features:
Aesthetic and corrosion-resistant surface; requires high-precision dies and embossing pressure; suitable for high-end decorative and functional applications
4.3Galvanized Embossed Plate
Common Patterns: Diamond, Striated, Ripple
Typical Products:
- Galvanized Diamond Plate Sheet
- Anti-Slip Galvanized Embossed Panel
- Galvanized Checker Plate for Flooring
- Striated Pattern GI Embossed Sheet
Applications:
Industrial flooring, anti-slip stair treads, outdoor platforms, machine guards, protective barriers
Process Features:
Offers corrosion resistance and mechanical strength; cost-effective; ideal for high-output embossing production

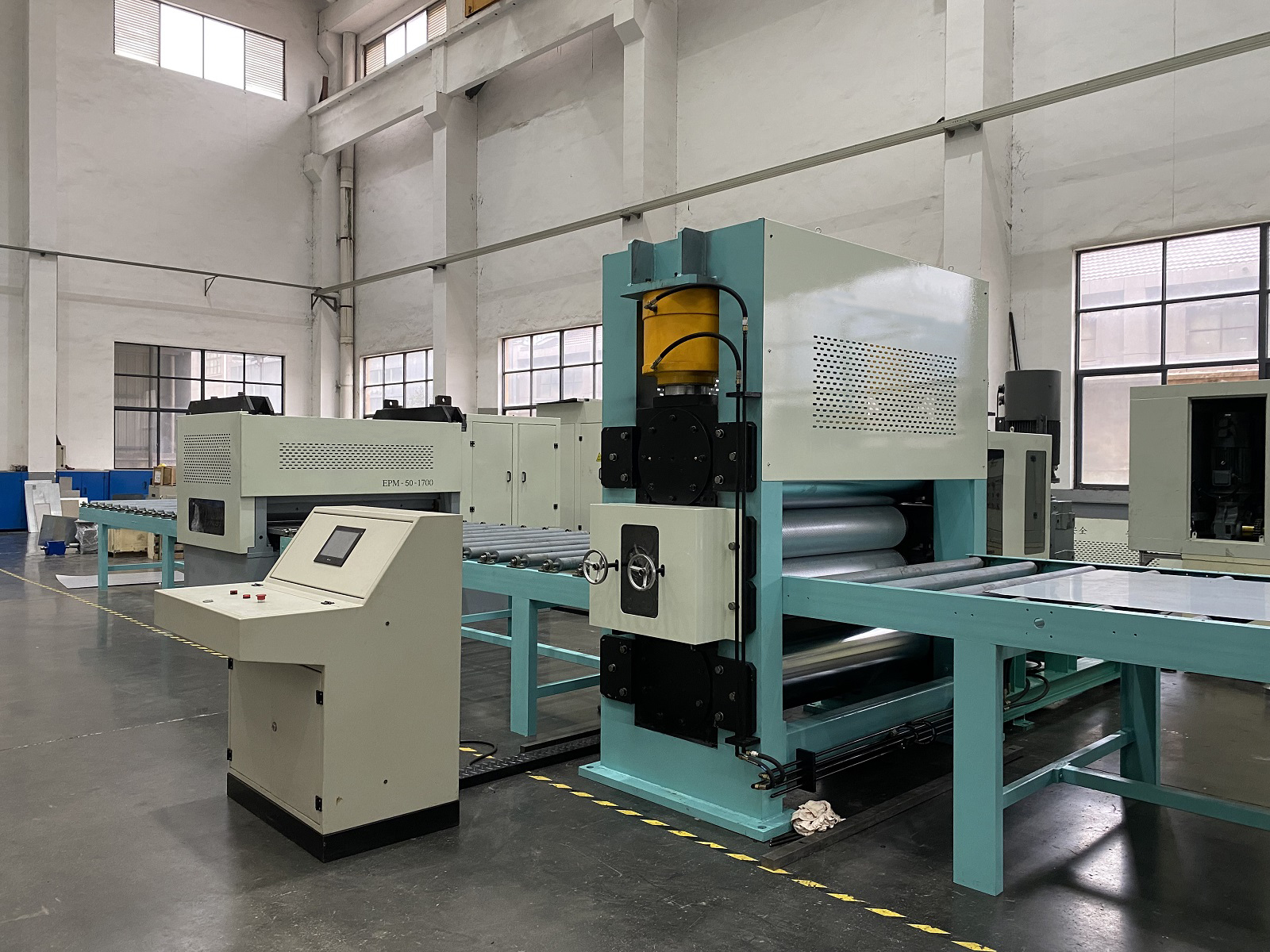
5.0Configuration of a Sheet Metal Embossing Production Line
A sheet metal embossing production line is an automated system designed to continuously emboss patterns onto metal coils or sheets. It combines multiple process stages—uncoiling, centering, embossing, cooling, leveling, cutting, and recoiling—into a single integrated line. The system is suitable for the continuous processing of various materials such as aluminum, stainless steel, and galvanized steel.
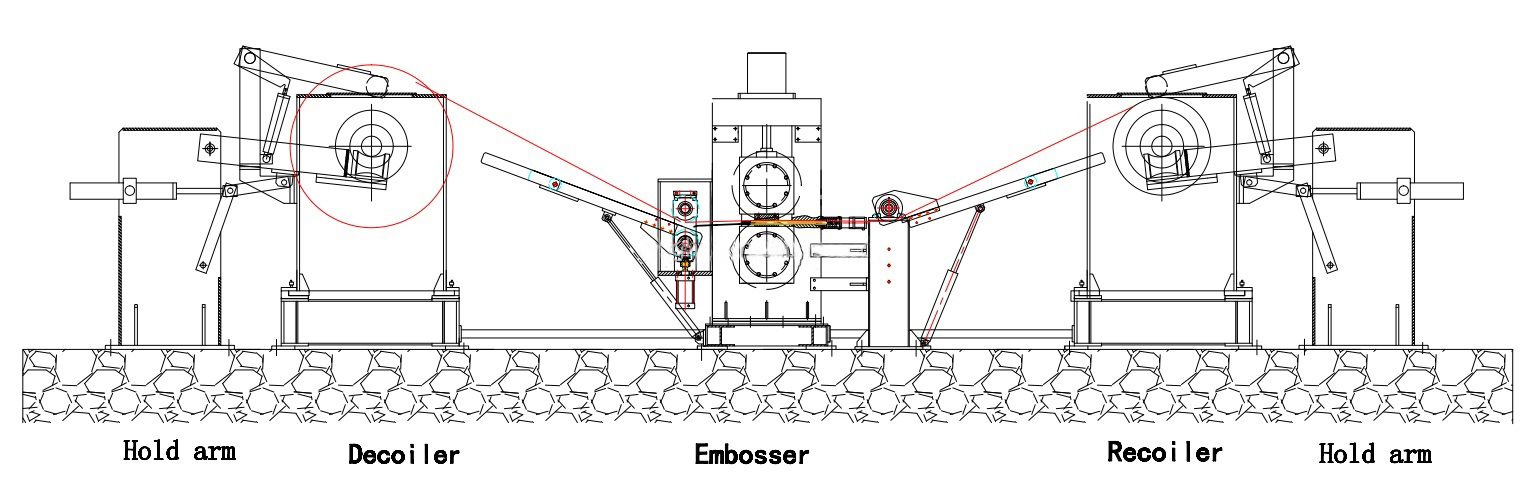
A typical metal embossing line includes the following modules:
- Uncoiler
Function: Holds and releases metal coils
Types: Hydraulic uncoiler, air-shaft uncoiler, double-head uncoiler - Centering & Tension Control System
Ensures stable material feeding, preventing misalignment and wrinkling - Embossing Unit
Structure: Pair of precision-engraved rollers, configured in male-female alignment
Function: Transfers patterns onto the metal surface via roller pressure
Drive Types: Mechanical, hydraulic, or servo motor-driven - Cooling Unit(Optional)
Used in high-speed production to manage roller temperature or cool the embossed material - Leveling Unit
Removes internal stresses and flattens the embossed sheet for downstream processing - Cut-to-Length or Slitting Unit
Cuts the embossed material into fixed-length sheets or strips as required - Recoiler
Rewinds the finished embossed strip for easy handling, packaging, and transport - Electrical Control System (PLC + HMI)
Provides full-line automation, supporting parameter tuning, pattern alignment, production counting, and more
6.0Advantages and Applications of Metal Embossing
Metal embossing is more than just an aesthetic enhancement—it offers several practical benefits:
- Enhanced Structural Strength and Rigidity:
Allows the use of thinner materials, reducing both cost and weight. - Improved Decorative Appeal:
Widely used in architectural finishes, appliance housings, and transportation infrastructure. - Upgrading Lower-Grade Materials:
Embossing can improve the appearance and value of secondary or downgraded coils. - Improved Surface Performance:
Enhances wear resistance, slip resistance, and contamination resistance.
Typical application areas include:
- Architectural curtain walls and interior decorative panels
- Elevator panels and metal ceilings
- Transportation equipment (train cars, interior cladding)
- Appliance housings
- Metal trays and storage cabinets used in the food industry
7.0Manufacturing Process of Diamond Plate
Diamond plate—also known as checker plate or tread plate—is a typical application of metal embossing. Its surface features a regular raised diamond pattern, offering excellent slip resistance.
Manufacturing Methods
- Stamping Method:
Commonly used for aluminum plates, where the sheet is passed between two rollers—one smooth and one engraved with a diamond pattern - Hot Rolling Method:
Used for steel plates, where the pattern is applied by a roller set at elevated temperatures.
Hot rolling helps reduce steel hardening and maintains good ductility.
Common Applications
- Industrial platforms, stair treads, and pedestrian ramps
- Truck bed flooring, toolbox panels
- Architectural decorative components, exterior furniture panels
Due to its high strength, excellent slip resistance, and cost-effectiveness, diamond plate is especially popular in safety-critical applications.
forming lines, or other processing units.
8.0How to Choose the Right Sheet Metal Embossing Machine
Different metal types, pattern requirements, and production capacities demand specific configurations for embossing machines. Key considerations include:
| Parameter | Requirements Description |
| Pressure System | Hydraulic or servo-driven systems selected based on sheet thickness |
| Die Design | Interchangeable dies to support various patterns; made from high-hardness, wear-resistant materials |
| Automation Level | Optional auto-feeding, discharging, and pattern alignment features |
| Material Compatibility | Support for a range of materials (aluminum, stainless steel, galvanized steel) and thicknesses |
With the rise of high-end demands in architecture, transportation, and home appliance sectors, embossed sheets are no longer limited to anti-slip functions. They are now widely used for decorative, branding, and custom design purposes.
Key technological trends include:
- Digital Pattern Design: CAD-based pattern input enables rapid switching and small-batch customization
- High-Precision Servo Control: Improves embossing consistency and reduces die wear
- Multi-Function Integration: Combines embossing, cutting, and coating in one production line
- Eco-Efficient Design: Lower energy consumption and minimal lubrication for greener manufacturing
9.0Conclusion
Metal embossing elegantly merges aesthetics with structural performance, making it a vital process in modern metal fabrication. Whether for decorative or functional purposes, the technology demonstrates strong adaptability and value. With continued advancements in equipment precision and process control, embossing is expanding into more industries and applications.
10.0Metal Embossing FAQ
How is metal embossing different from embossing on plastics or coatings?
Metal embossing deforms the metal base material itself, altering its surface shape and performance, whereas embossing on plastics or coatings only affects the surface layer without changing the substrate.
What types of machines are used for metal embossing?
Common machines include roll-to-roll embossing machines for continuous coil processing, sheet embossing machines for individual metal sheets, integrated embossing units embedded in production lines, and manual or semi-automatic machines for prototyping or small batches.
What metal materials are suitable for embossing?
Aluminum, stainless steel (such as 304 and 201 grades), and galvanized steel are typical choices. Selection depends on application requirements, corrosion resistance, and forming characteristics.
What are typical embossing patterns?
Aluminum often features five bar, orange peel, diamond, and checker patterns; stainless steel includes water ripple, small bead, linen, and leather textures; galvanized sheets commonly have diamond, striated, and ripple patterns.
What is diamond plate, and where is it used?
Diamond plate (also called checker or tread plate) has a raised diamond pattern providing excellent slip resistance. It’s widely used for industrial flooring, stair treads, truck beds, toolboxes, and architectural elements.







