1.0Introduction
Metal pipes are widely used across various industries, including aircraft manufacturing, engineering machinery, transportation, petrochemicals, guardrail fabrication, and agricultural and livestock sectors.
Pipes and tubes come in various materials, requiring different cutting techniques and tools.
Mastering pipe cutting improves project quality, safety, and efficiency, whether in industrial, professional, or DIY settings.
1.1Factors Influencing Cutting Methods
- Pipe material (steel, plastic, etc.)
- Pipe thickness and diameter
- Required precision and finish
1.2 Pipe and Tube Cutting Tools Overview
- Manual & Convenient Tools: Hand-operated tools like pipe cutters and hacksaws, ideal for small-scale projects where portability, simplicity, and low cost are key.
- Electric Cutting Tools: Powered tools such as angle grinders, chop saws, and reciprocating saws, offering faster cutting speeds for medium-sized jobs with moderate precision.
- Specialized Cutting Tools: Precision-focused machines like band saws and cold saws, designed for continuous operation and high-quality cutting in industrial settings.
- Portable Tools: Compact, lightweight solutions like portable band saws, perfect for on-site cutting, especially in confined or hard-to-reach spaces.
- High-End Cutting Tools: Advanced equipment like horizontal bandsaws, vertical bandsaws, and laser cutting machines, delivering high precision and efficiency for complex, large-scale work.
- Flame Cutting Tools: Traditional methods like oxy-acetylene and plasma cutting, effective for thick metal sections where speed matters.
Different projects and materials require different types of tools, from manual cutters for small jobs to advanced laser and plasma machines for industrial production. Below is a comprehensive comparison of various cutting tools, highlighting their suitable applications, features, safety ratings, and price indexes to help you select the best tool for your needs.
| Category | Tool Name | Suitable for | Features | Safety | Price Index |
| Manual & Convenient Tools | Pipe & Tube Cutter | Small projects, no electricity needed | Compact, inexpensive, ideal for thin-walled pipes | ☆☆☆☆☆ | ☆ |
| Hacksaw | Simple cutting, small projects | Manual tool, simple cuts but slower and less precise | ☆☆☆☆☆ | ☆ | |
| Electric Cutting Tools | Angle Grinder | Quick cutting, medium projects | Electric tool, fast cuts but higher safety risks | ☆☆☆ | ☆☆ |
| Chop Saw | Medium projects, rough metal cutting | Electric tool, efficient cutting but needs support | ☆☆☆☆ | ☆☆☆☆ | |
| Miter Saw | Precise angle cutting, custom work | Precise angle cuts, ideal for customized jobs | ☆☆☆☆ | ☆☆☆☆ | |
| Reciprocating Saw | Quick, rough cutting of metal pipes | Versatile, fast rough cuts, less precise than saws | ☆☆☆ | ☆☆☆ | |
| Specialized Cutting Tools | Band Saw Cutting | Medium to large projects, precision cuts | High precision, ideal for continuous cutting | ☆☆☆☆☆ | ☆☆☆☆☆ |
| Cold Saw | High precision, no heat-affected zones | High precision, no heat-affected zones, ideal for surface-sensitive cuts | ☆☆☆☆☆ | ☆☆☆☆☆ | |
| Portable Tools | Portable Band Saws | On-site cutting, limited workspace | Portable, ideal for electricians and tradespeople | ☆☆☆☆☆ | ☆☆☆☆ |
| High-End Cutting Tools | Horizontal Bandsaw | Large pipe cutting, precise work | High precision, ideal for large pipe cutting | ☆☆☆☆ | ☆☆☆☆☆ |
| Vertical Bandsaw | Complex shapes, custom cutting | High precision, ideal for complex and fine cuts | ☆☆☆☆ | ☆☆☆☆☆ | |
| Laser Tube Cutting Machine | High precision cutting, complex shapes | High precision, ideal for complex designs and mass production | ☆☆☆☆☆ | ☆☆☆☆☆ | |
| Flame Cutting Tools | Oxy/Acetylene Torch | Thick metal cutting, rough cuts | Flame cutting, low precision, needs post-processing | ☆☆ | ☆☆☆☆ |
| Plasma Pipe Cutting Machine | Thick metal cutting, higher precision | High precision, needs post-processing | ☆☆ | ☆☆☆☆ |
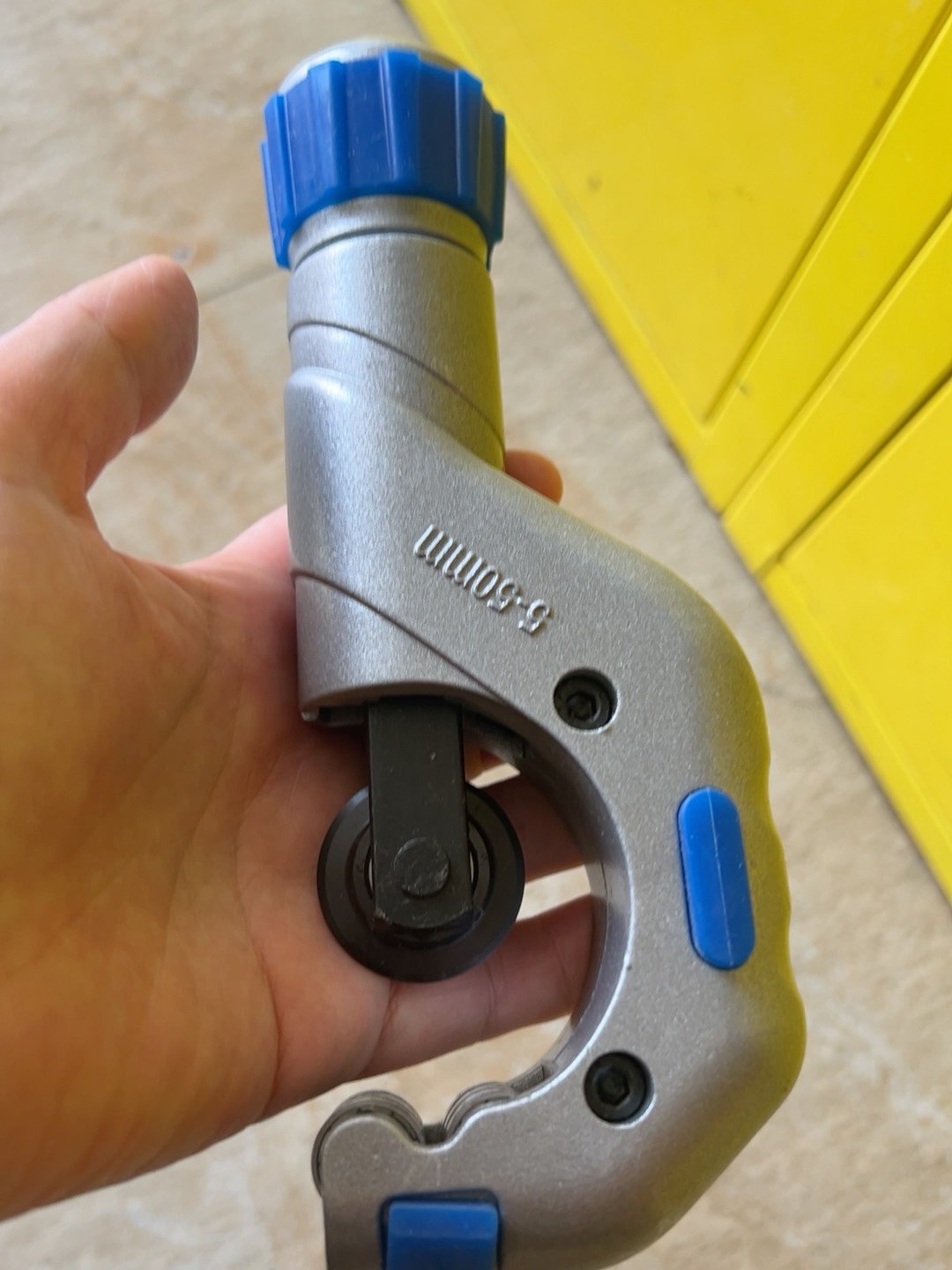
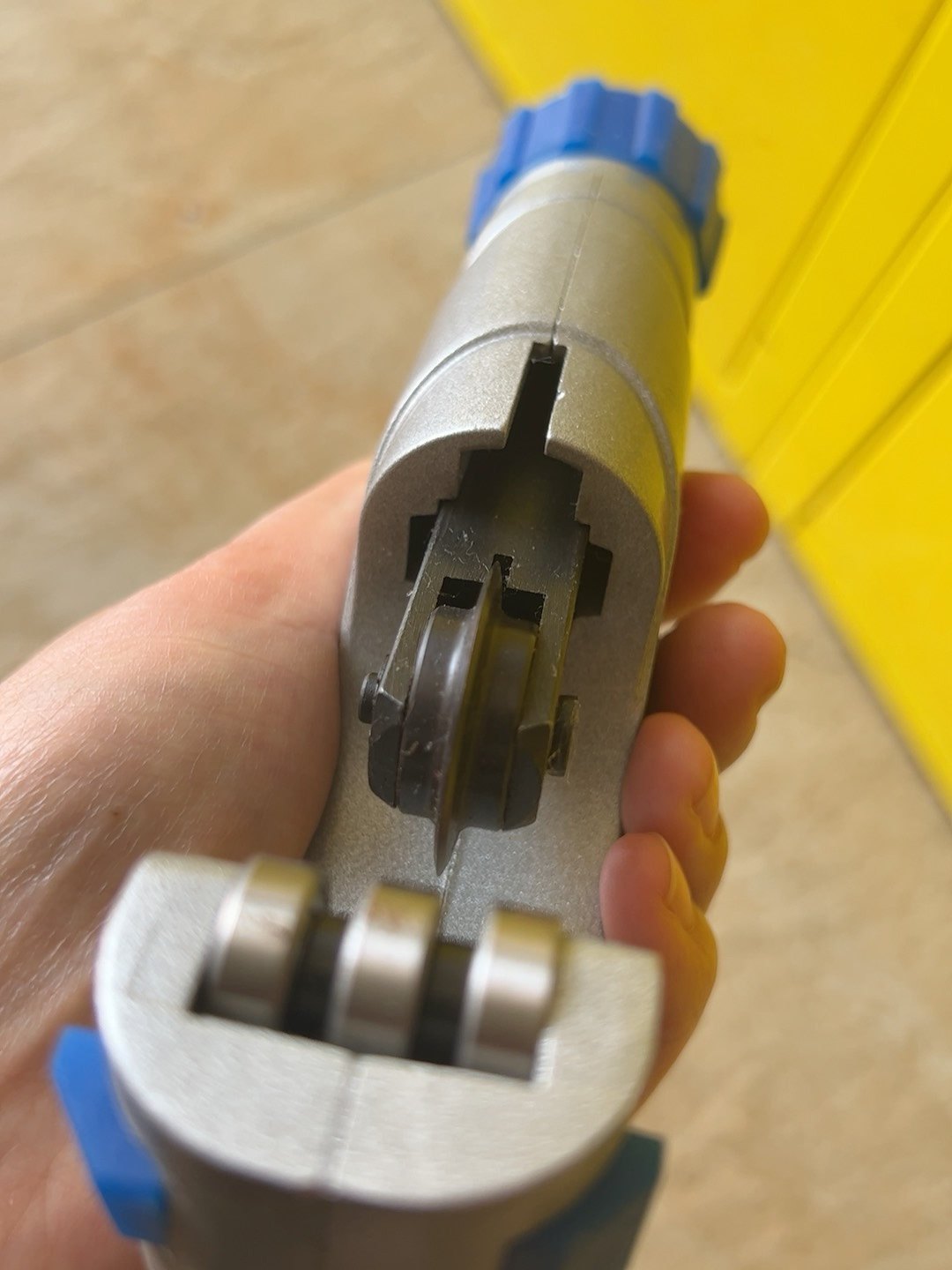
2.0Pipe & Tube Cutter
It’s very approachable and easy to use, and is often my go-to cutting tool for smaller projects that only require a dozen or so cuts. Because it doesn’t require electricity, you can use it anywhere you want, whether it’s in the garden, in the woods, in your living room, or pretty much anywhere else. The cutting wheel, of course, is fairly sharp, but overall it’s the safest option out of all the ones that we’ll talk about today.


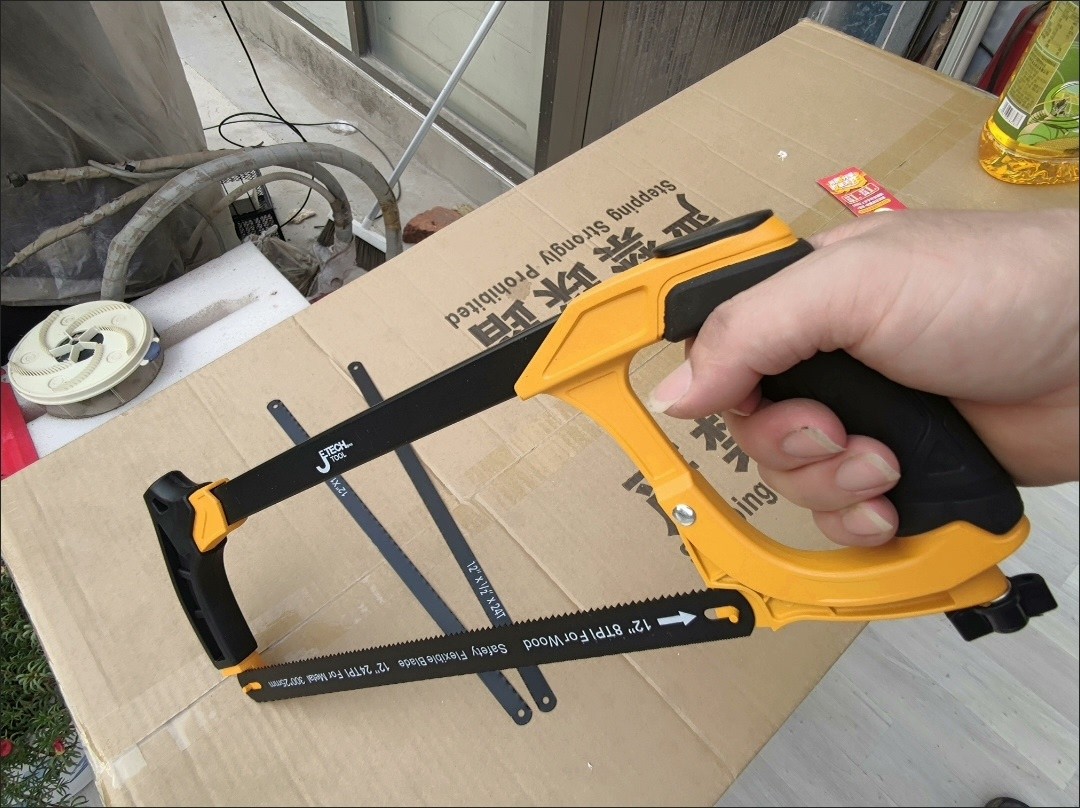
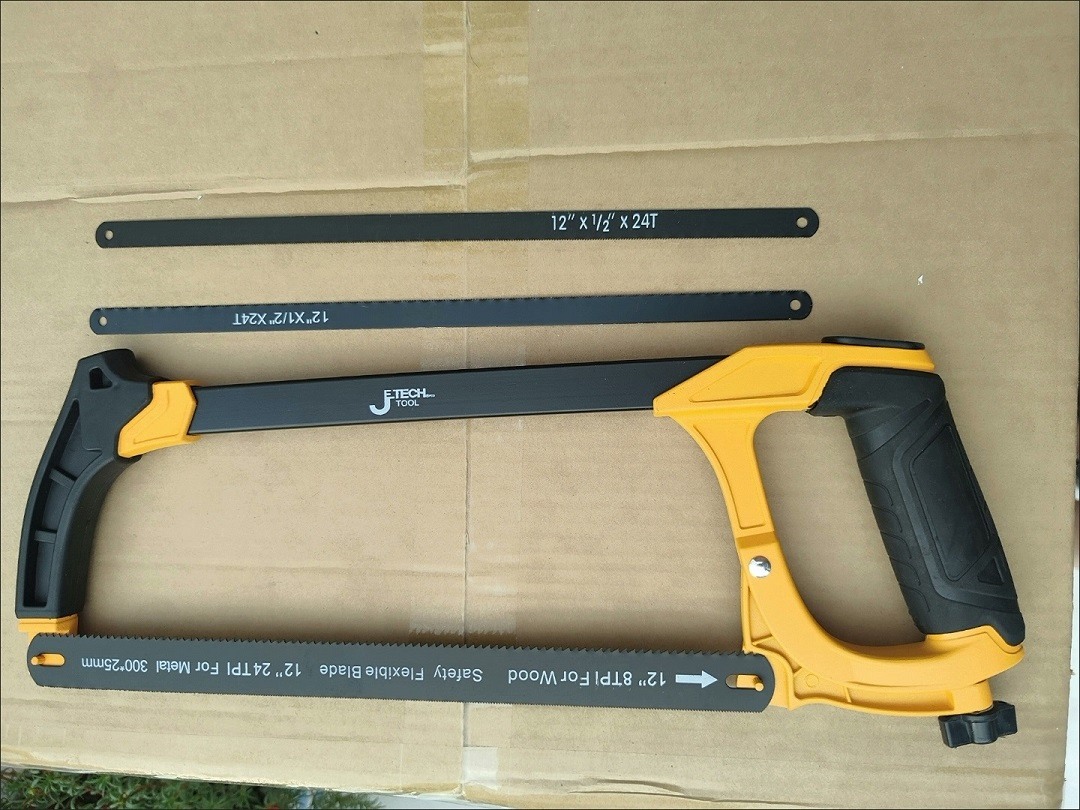
3.0Hacksaw
A hacksaw can provide many of the same benefits as tubing cutters while also being a quicker alternative. It is still approachable, non-powered, compact, versatile, and fairly inexpensive, especially if you already have a hacksaw that allows you to swap out the blades. Make sure to get a blade or hacksaw combo designed specifically for cutting metals like steel. Go for a thin blade with at least 24 TPI (teeth per inch).


4.0Angle Grinder
Angle grinders are incredibly useful and often capable of performing tasks that no other saw can. However, cutting metal pipes isn’t one of them. The speed and safety risks make angle grinders a less favorable option for cutting thin-walled metal pipes. If you must use one, ensure that the cutting wheel is at least 4” in diameter and designed specifically for steel.
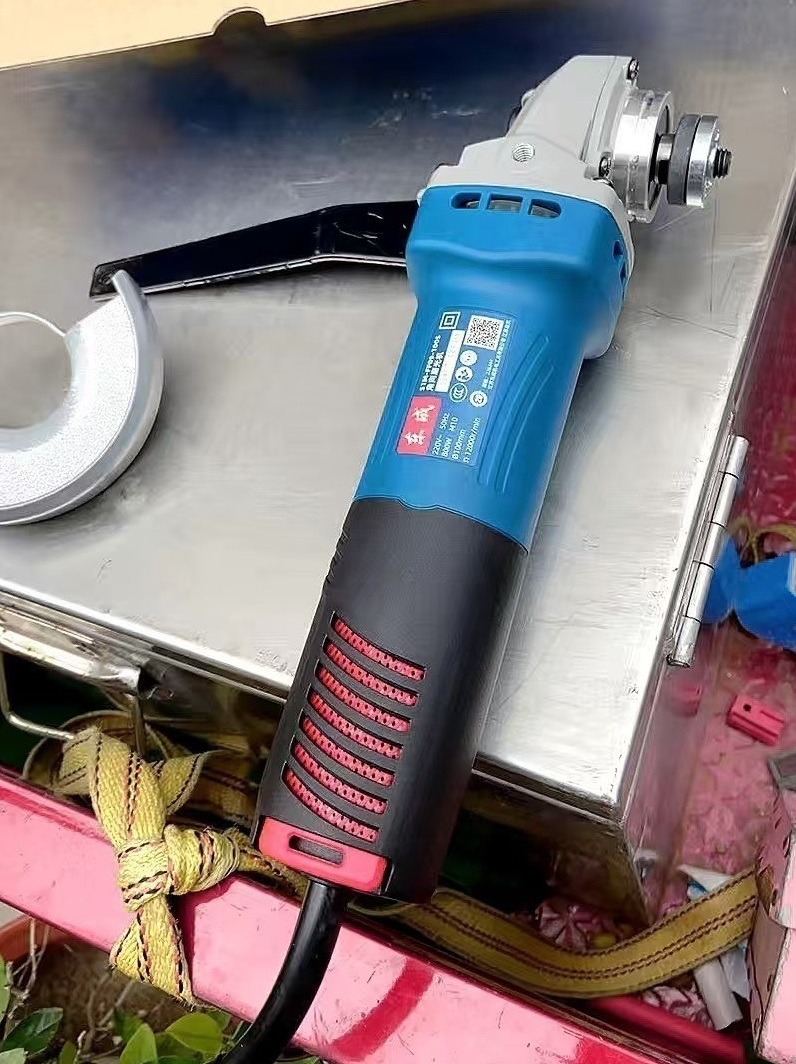


5.0Chop Saw
A chop saw can also be used to cut conduit if you swap the standard blade for an abrasive one designed for cutting metal. This will give you fast and clean cuts, but you’ll need a dedicated workbench or a large enough space for setup.
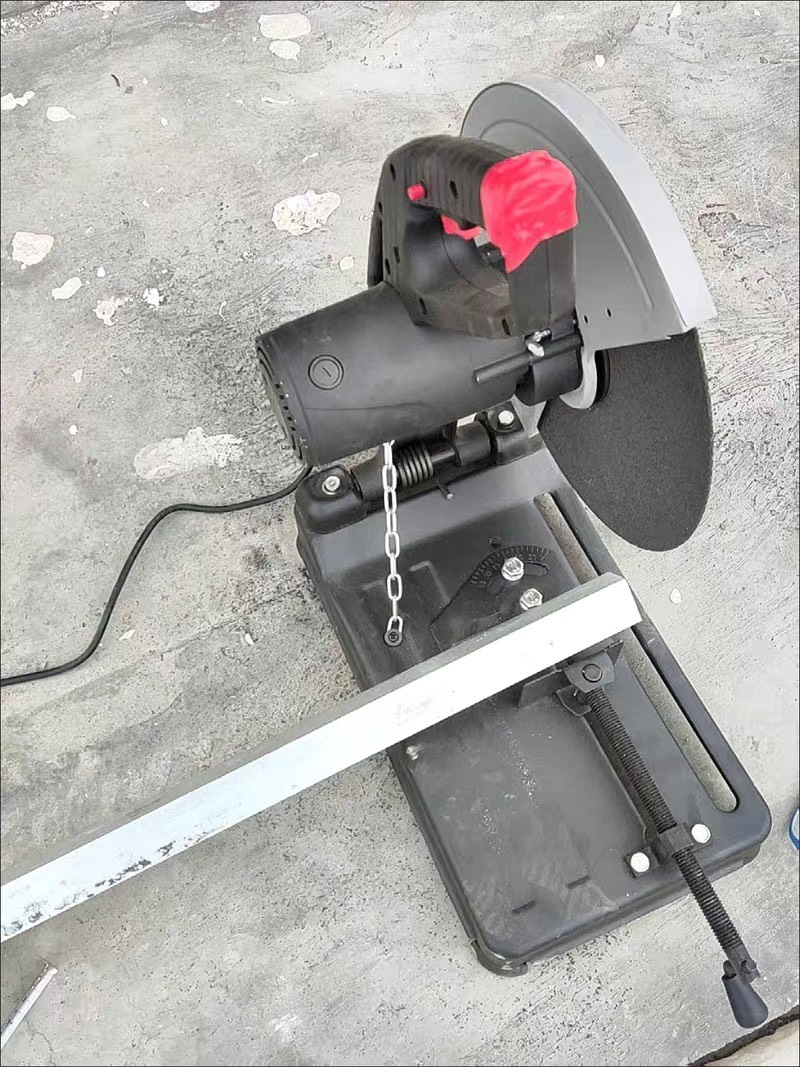
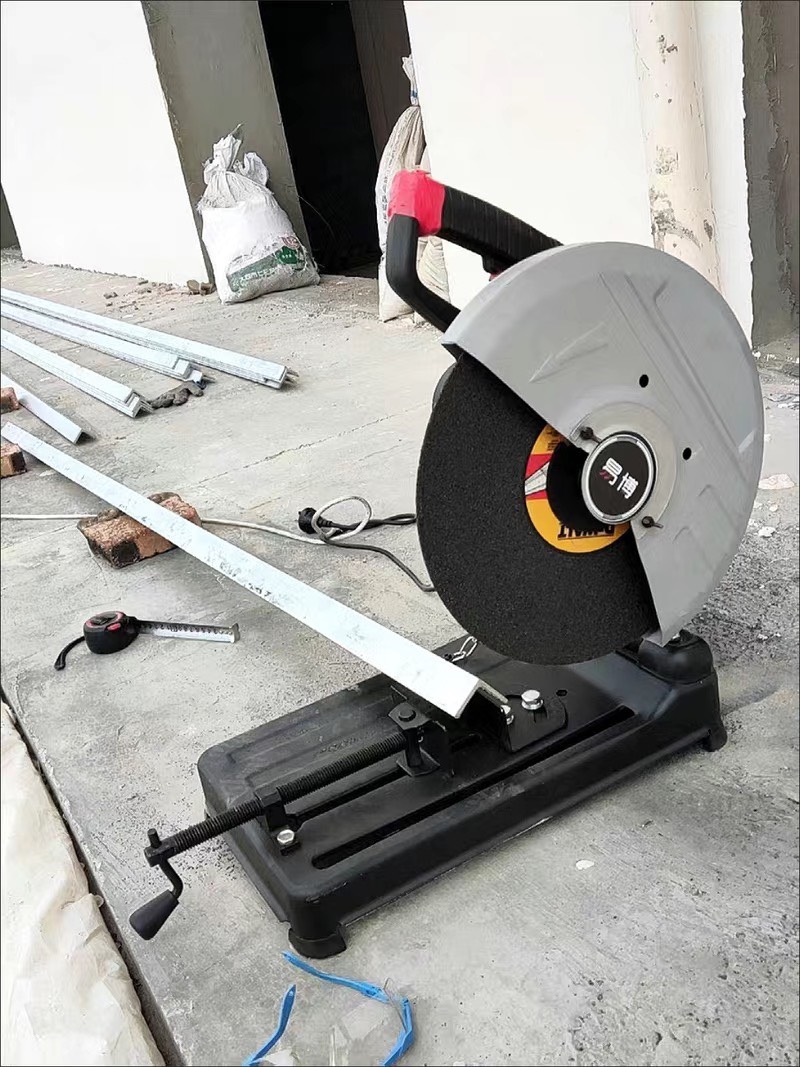


6.0Miter Saw
Similar to the chop saw, a miter saw is designed for cutting precise angles, which is useful when you’re welding pipes or creating angled structures. But why use a miter saw for cutting metal pipes? It might be beneficial if you already own one and can buy the proper blades.
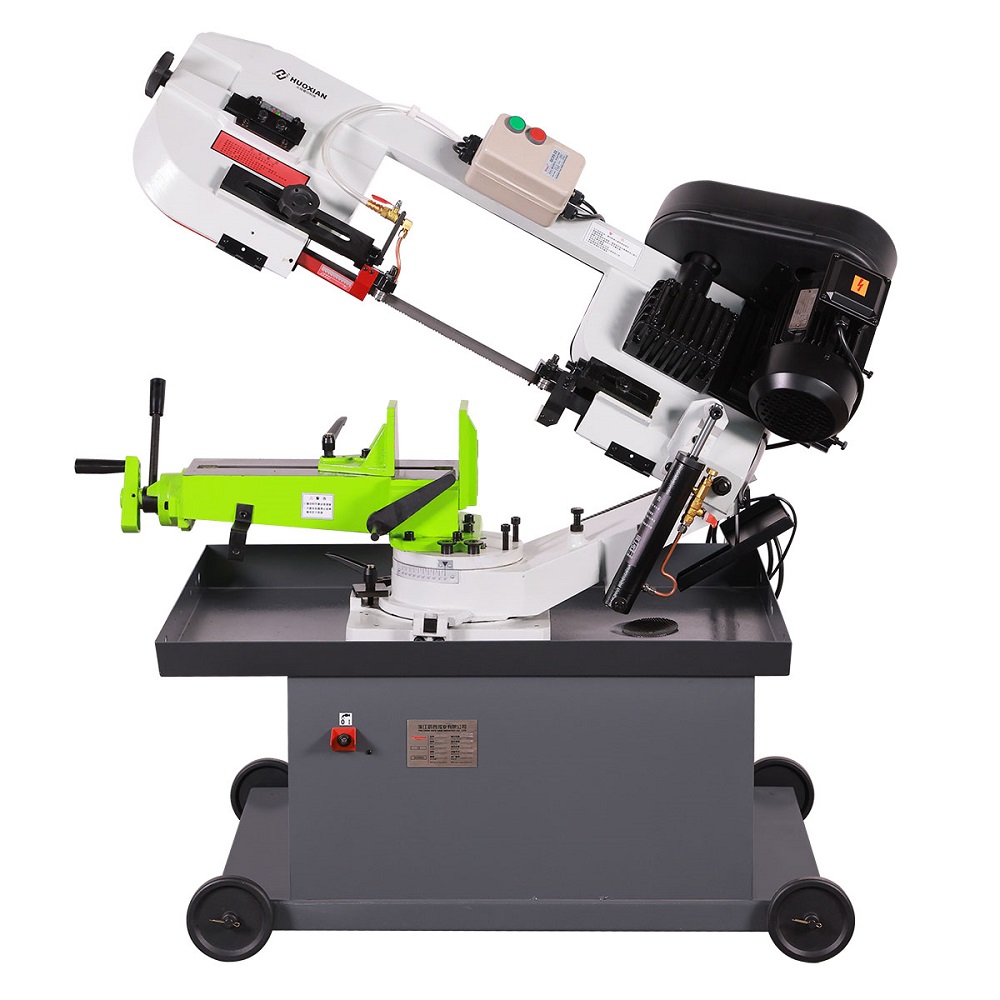
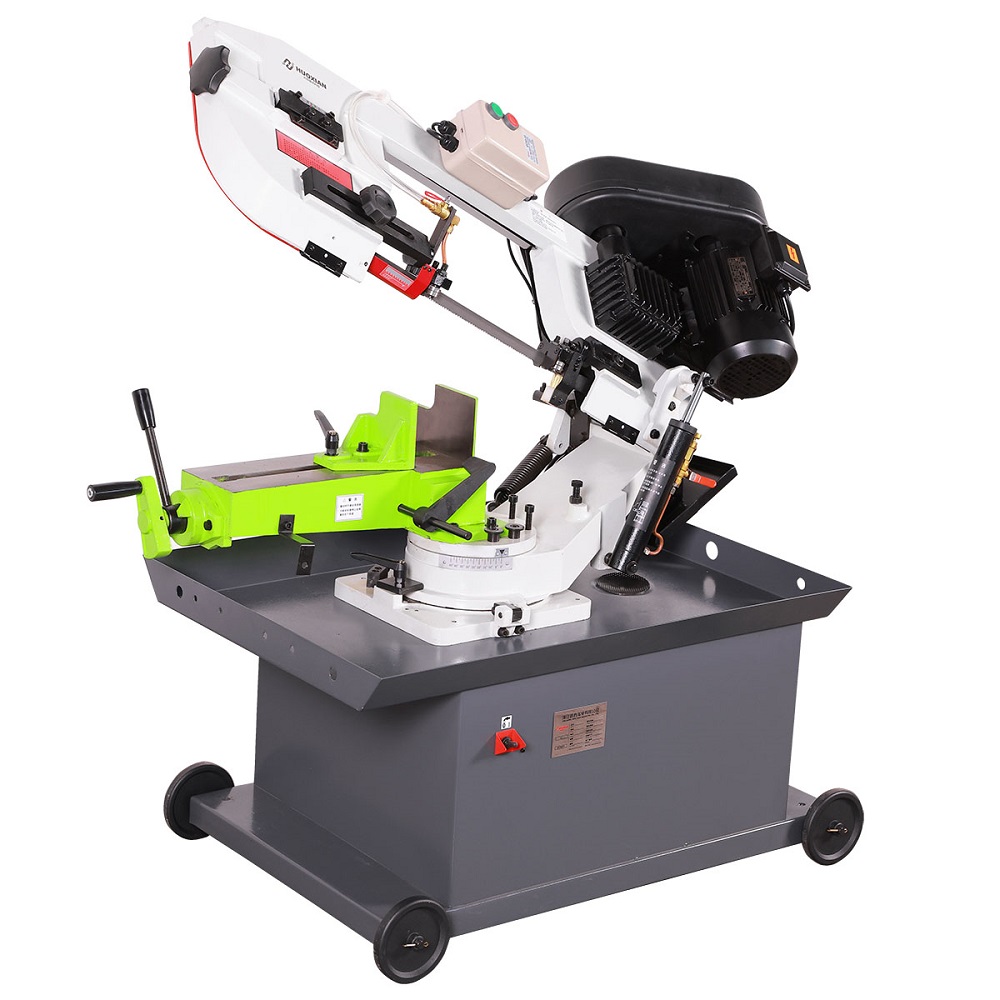
7.0Band Saw Cutting
A band saw is an electronic cutting technique that uses a seamless band blade with tooth contours to cut pipe materials. The blade moves vertically or horizontally on two mounting wheels.
It is a versatile saw used for cutting both wood and metal stock, as well as trimming meat. The blade runs on two pulleys—the driver and the idler—and passes through a work table where material is manually fed. To cut, the operator must hand-feed and manipulate the stock against the blade.
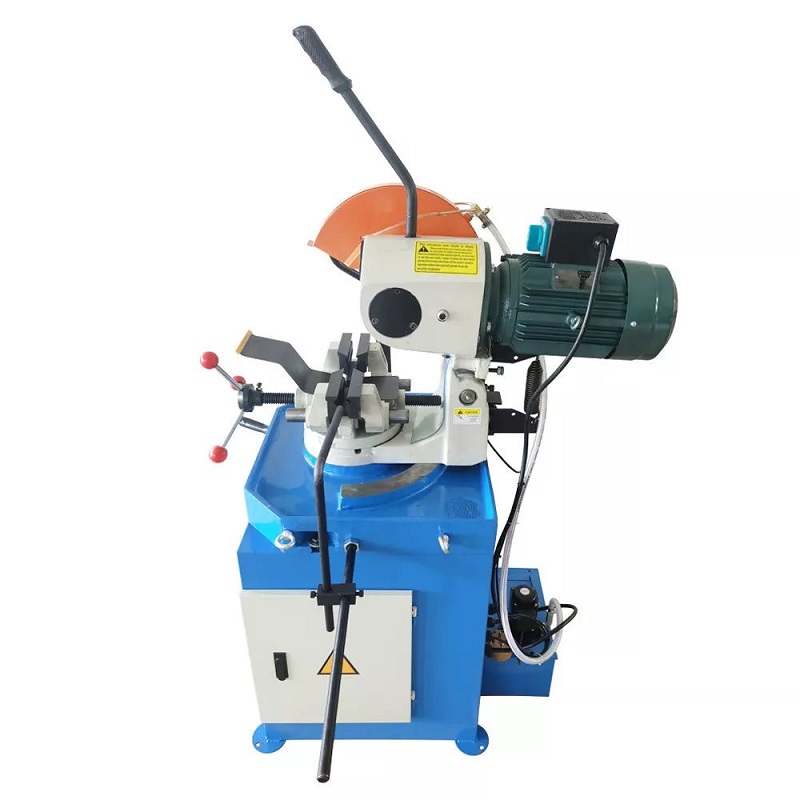
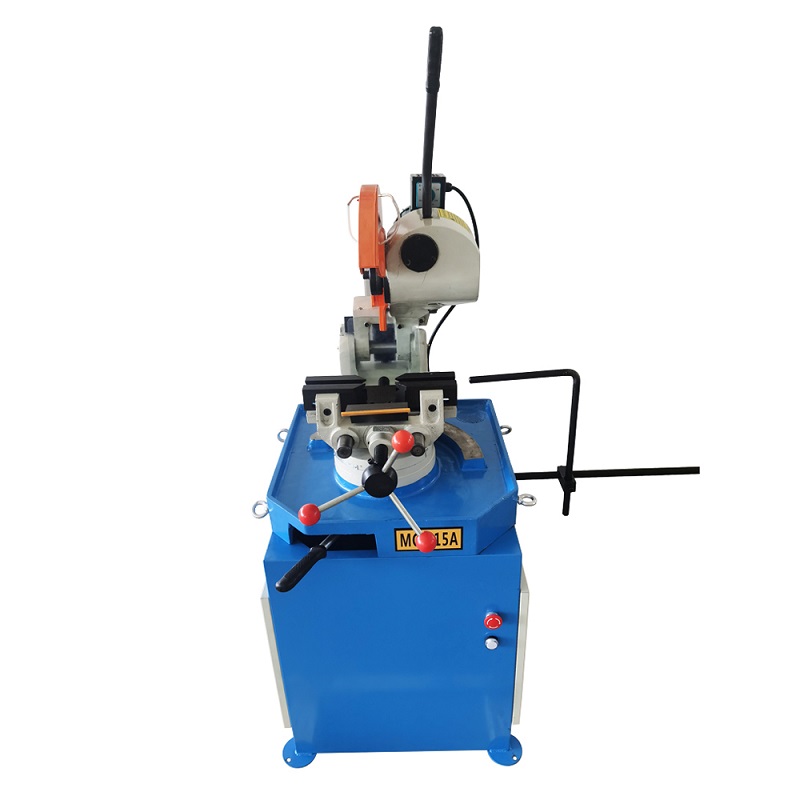
8.0Cold Saw
Cold saw cutting involves a rotating blade that directly contacts the pipe or tube material to make the cut. This process is popular because it leaves no heat-affected zones on the pipe surfaces.
Cold saws are ideal for industrial use, providing clean cuts without excessive heat generation. They are suitable for perpendicular cutting only. The toothed blade transfers the heat generated during cutting to the chips, allowing both the blade and material to remain cool.
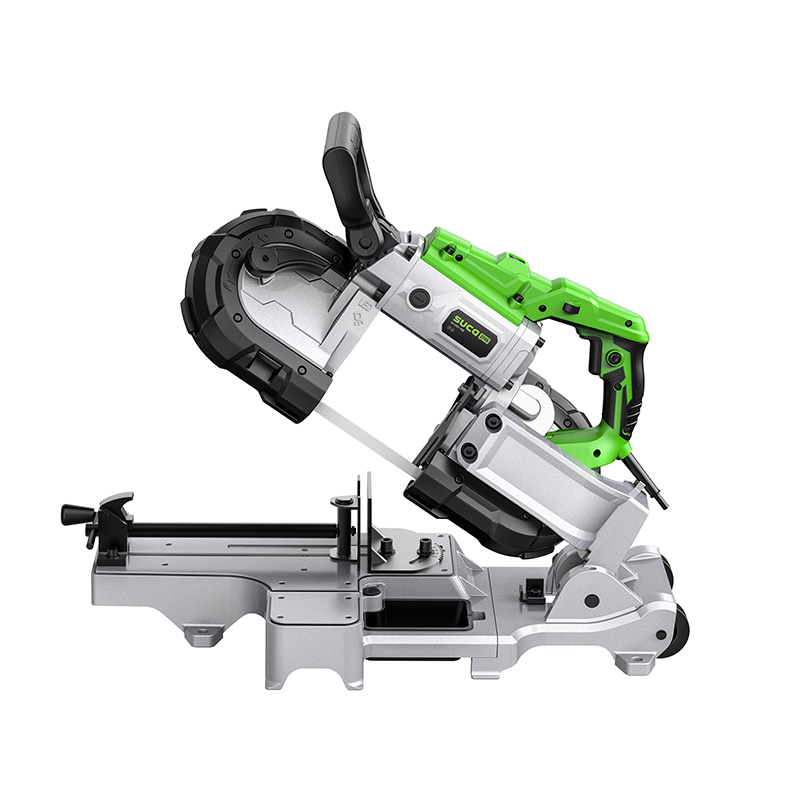
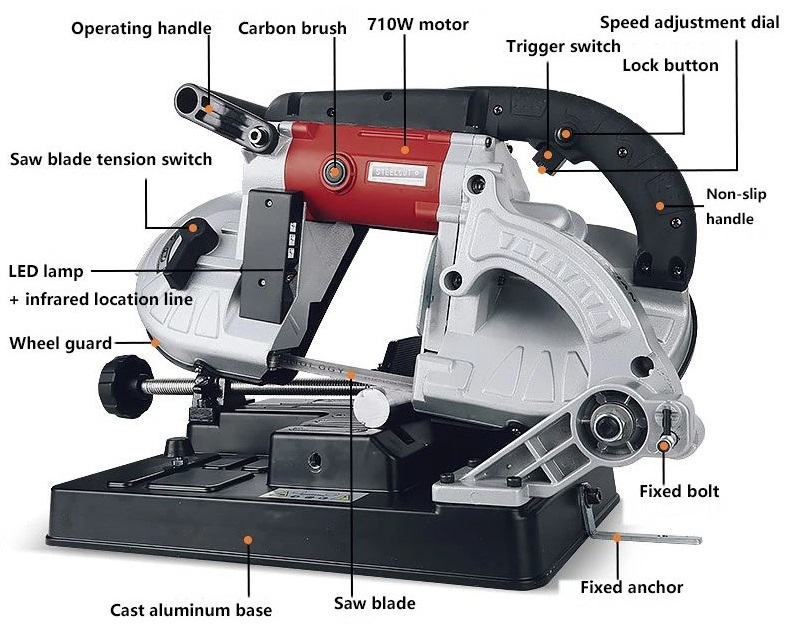
9.0Portable Band Saws
Portable band saws are battery-powered tools that are more accessible than traditional band saws. They are compact and ideal for cutting thin-walled pipes and tubes. These are commonly used by electricians and other tradespeople for convenience and speed.
10.0Reciprocating saws
Reciprocating saws are a versatile tool for cutting metal pipes, especially thin-walled and medium-thickness types.
Equipped with the right metal-cutting blade (14–24 TPI), they offer fast, efficient cutting for rough applications.
While they can handle thick-walled pipes, the cuts may be slower and less smooth compared to cold saws or laser cutters.
Ideal for on-site work, repairs, and demolition, reciprocating saws deliver flexibility and speed where precision is less critical.


11.0Horizontal Bandsaw
For square or round tubing, the horizontal bandsaw is a top choice. It allows for quick, accurate cuts with sturdy clamps that ensure precision. Midrange models feature coolant/lubricant systems for blade longevity.
12.0Vertical Bandsaw
Vertical band saws use a thin, ribbon-like metal loop with teeth directed downward to cut materials. Unlike other fixed shop saws, vertical band saws can make three types of cuts:
- Cross cuts or “cutoffs” – cuts made perpendicular to the long axis of the workpiece.
- Vertical bandsaws are excellent for fabricators working on precise parts, such as brackets. A high-quality model features a variable speed drive and the ability to weld blades, offering both accuracy and flexibility.


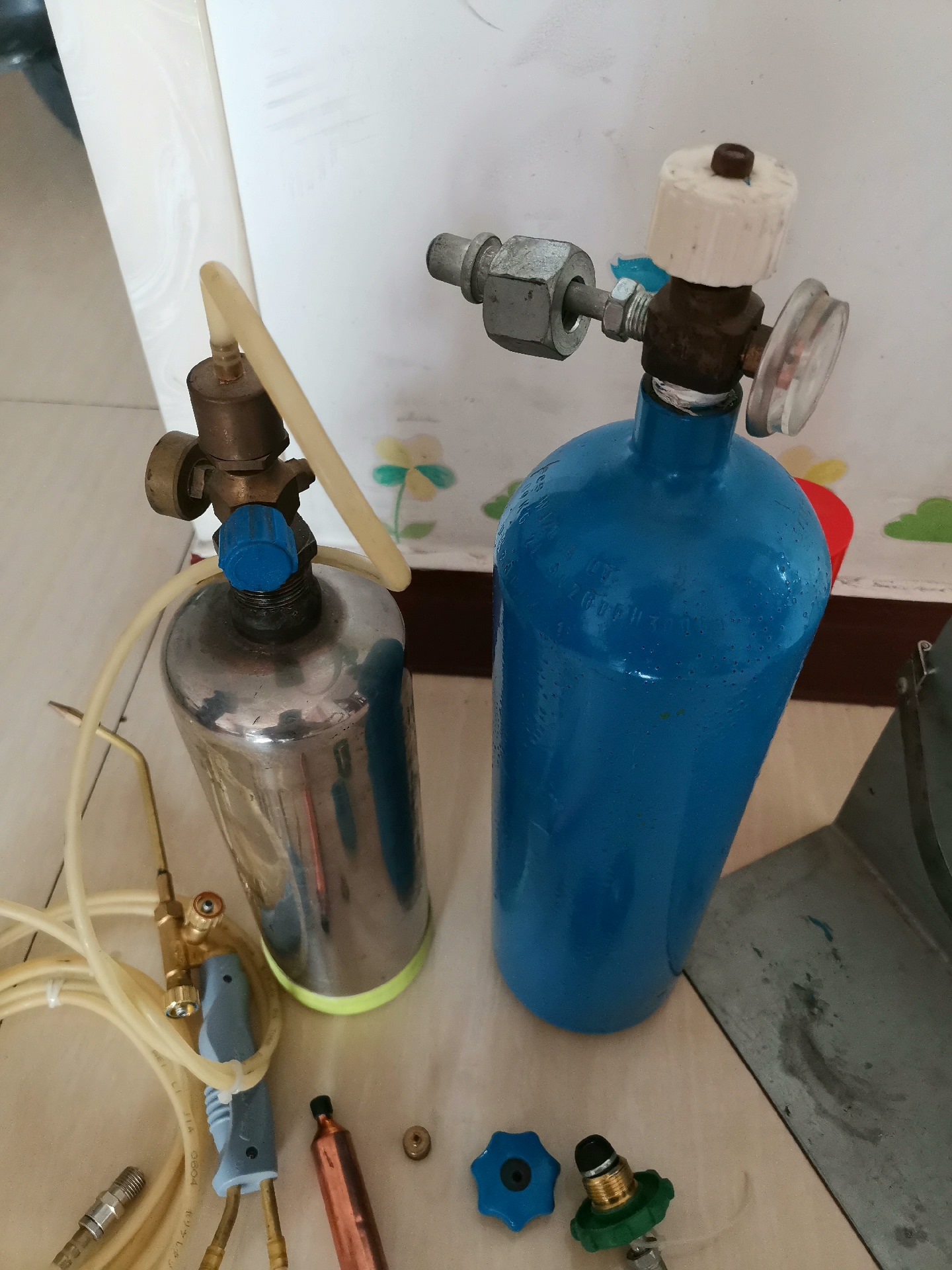
13.0Oxy/Acetylene Torch
While cutting metal with fire can be exciting, the oxy/acetylene torch is used as a last resort due to its risks and lack of accuracy. It is most useful for rough cuts and for heating rusted fasteners.


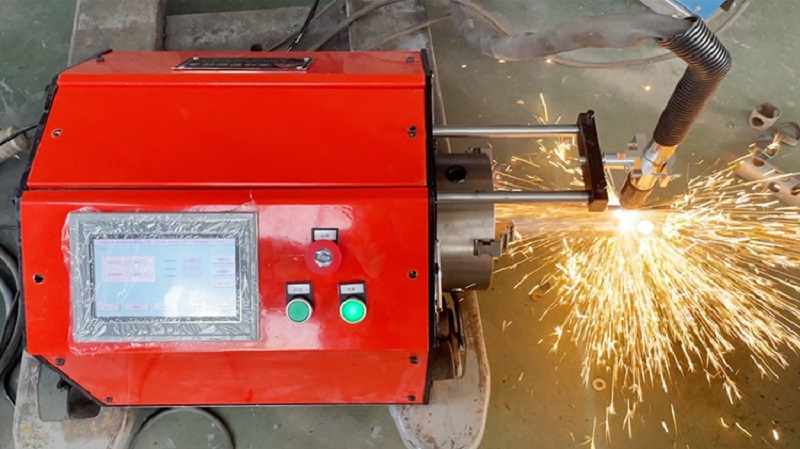
14.0Plasma Pipe Cutting Machine
Plasma pipe cutting machines are ideal for making precise cuts in metal pipes. They utilize a high-temperature plasma arc to melt through the material, leaving clean, accurate cuts. While the process is efficient, some cleanup may still be required.
CNC plasma pipe cutting machines use a high-velocity jet of ionized gas (plasma) to cut through metal pipes with precision. The operator inputs design specifications into the CNC system, allowing for automated, precise cuts tailored to specific requirements.
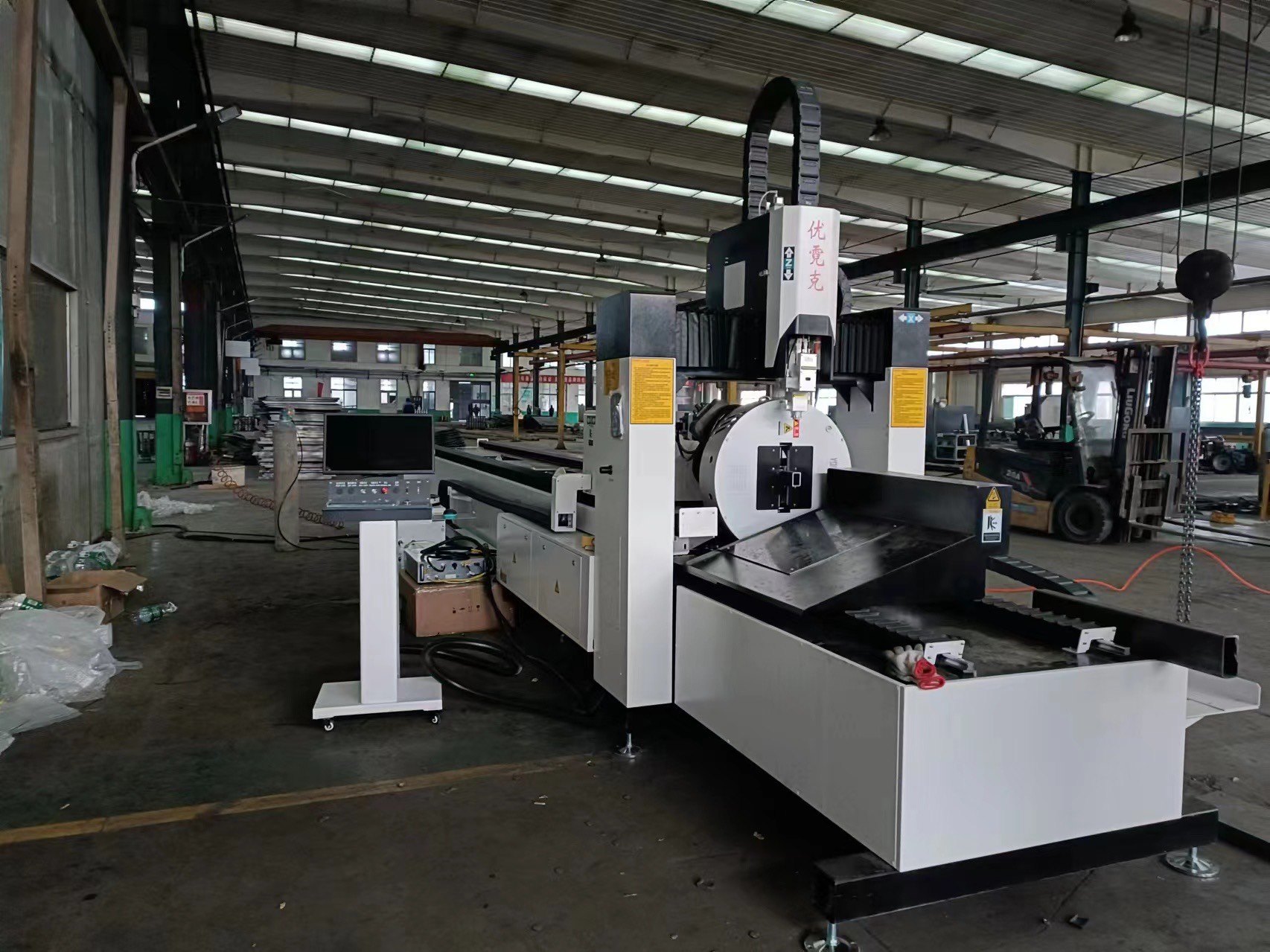
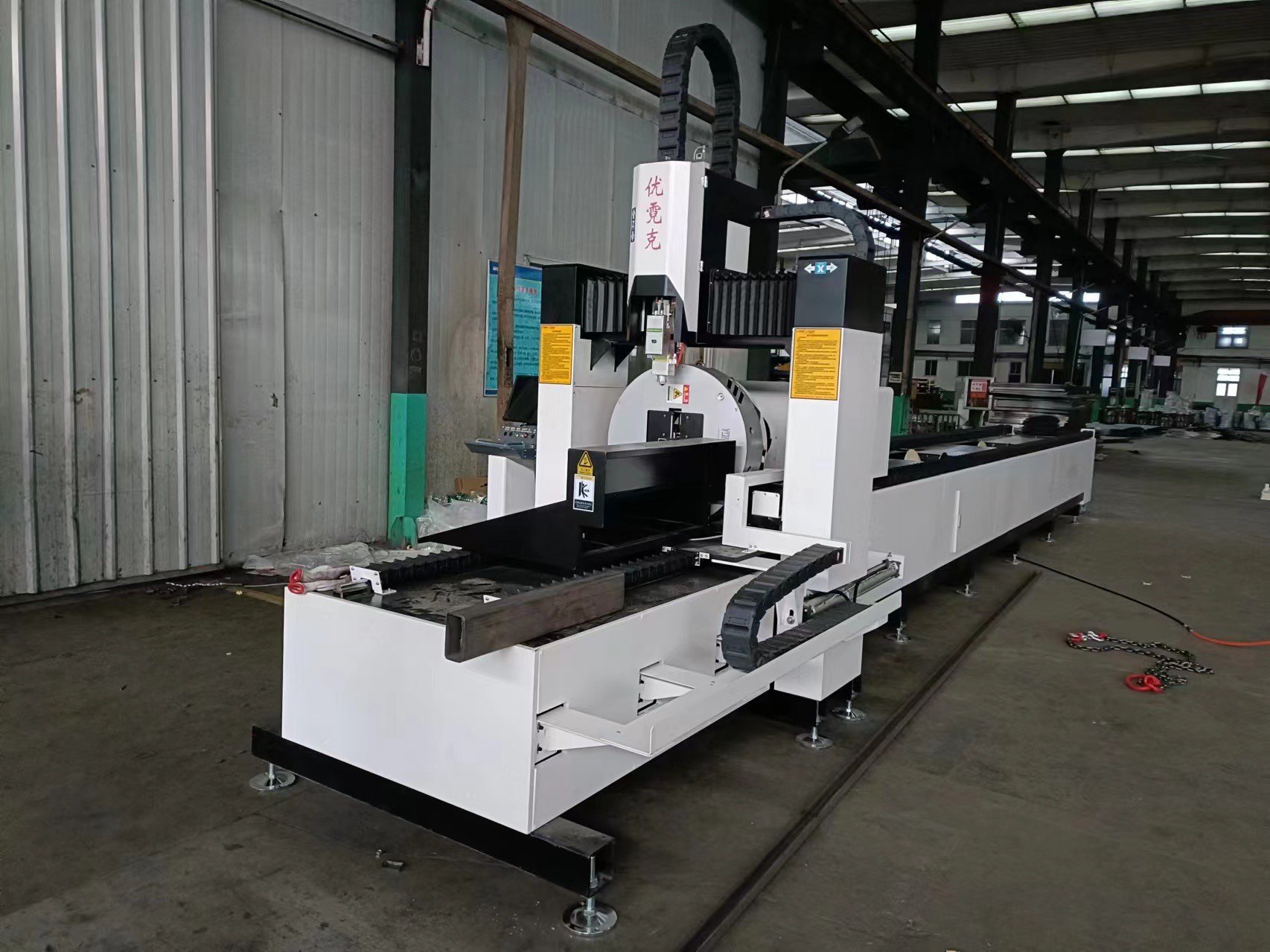
15.0Laser Tube Cutting Machine
Laser tube cutting is a precision machining process that uses a high-powered laser to cut through various types of metal or plastic tubes with exceptional accuracy and efficiency.
The laser beam melts the material as it cuts, leaving clean edges without burrs. This process is perfect for making complex cuts and intricate designs, offering both precision and speed in tube cutting.


References:
https://www.woodwardfab.com/blog/different-pipe-and-tube-cutting-techniques-and-equipment-discussed/
https://www.angi.com/articles/how-to-cut-metal-pipe.htm