
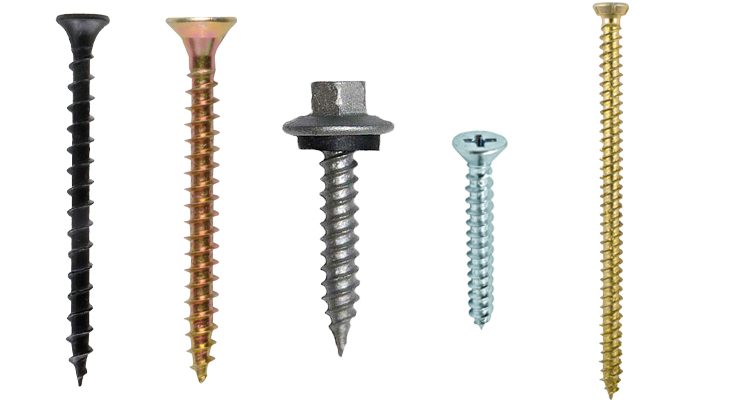
- 1.0Tapered-Shank Fasteners: Versatile Self-Tapping Design
- 1.1Chipboard Screw (Particle Board Screw)
- 1.2Concrete Screw (Tapcon / Masonry Screw / Confast / Blue Screw / Titen)
- 1.3Deck Screw
- 1.4Double-Ended Screw / Hanger Bolt
- 1.5Drive Screw (Hammer Drive Screw)
- 1.6Drywall Screw
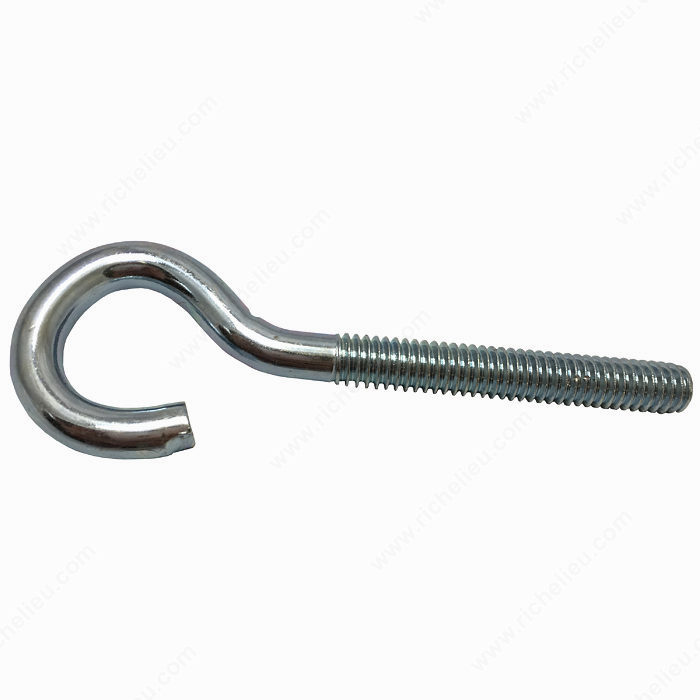
- 1.7Eye Screw (Screw Eye)
- 1.8Lag Bolt (Lag Screw / Coach Screw)
- 1.9Self-Drilling Wood Screw
- 1.10MDF Screw
- 1.11Plastic Self-Tapping Screw
- 1.12Mirror Screw
- 1.13Sheet Metal Screw
- 1.14Twinfast Screw
- 1.15Wood Screw
- 1.16Security Head Screw
- 2.0Non-Tapered Shank Fasteners: Precision & Heavy-Duty Applications
- 2.1Anchor Bolt
- 2.2Breakaway Bolt
- 2.3Cap Screw
- 2.4Socket Screw (Allen Bolt / Socket Head Cap Screw)
- 2.5Carriage Bolt (Cup Head Bolt / Coach Bolt)
- 2.6High-Temperature & High-Pressure Bolt
- 2.7Micro Precision Screw
- 2.8Anti-Vibration Locking Bolt
- 2.9Marine-Grade Bolt
- 2.10Confirmat Screw
- 2.11Elevator Bolt
- 2.12Eye Bolt
- 2.13Hex Cap Screw
- 2.14Fine Adjustment Screw
- 2.15Machine Screw
- 2.16Stove Bolt (Gutter Bolt)
- 2.17Plow Bolt
- 2.18Self-Drilling Screw (Tek Screw)
- 2.19Self-Tapping Machine Screw
- 2.20Set Screw (Grub Screw)
- 2.21Shoulder Bolt (Stripper Bolt)
- 2.22Tension Control (TC) Bolt
- 2.23Thread Rolling Screw
- 2.24Sex Bolt (Chicago Screw)
- 2.25U-Bolt / J-Bolt
- 2.26Hook Bolt
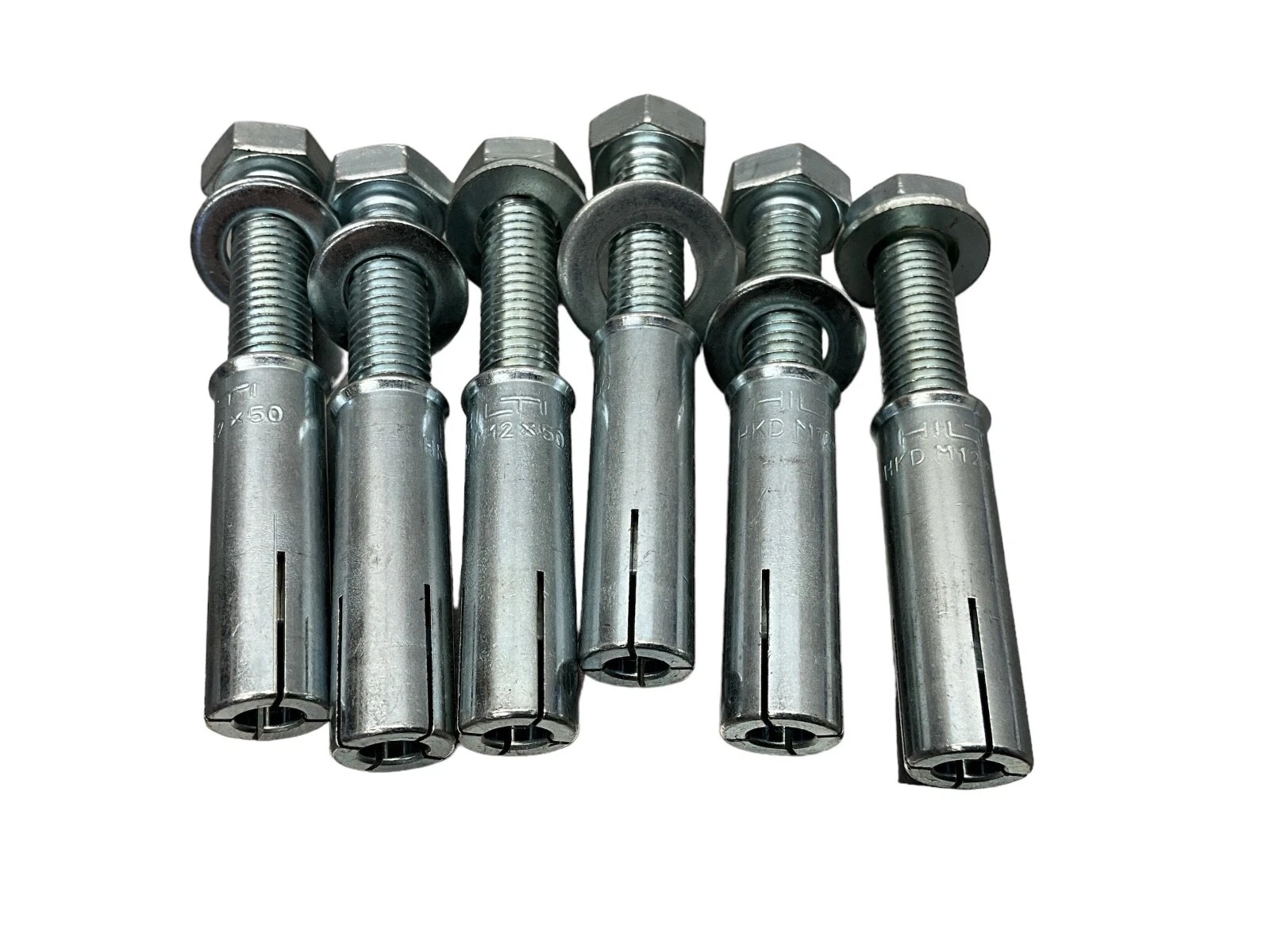
- 2.27Expansion Bolt (Dynabolt)
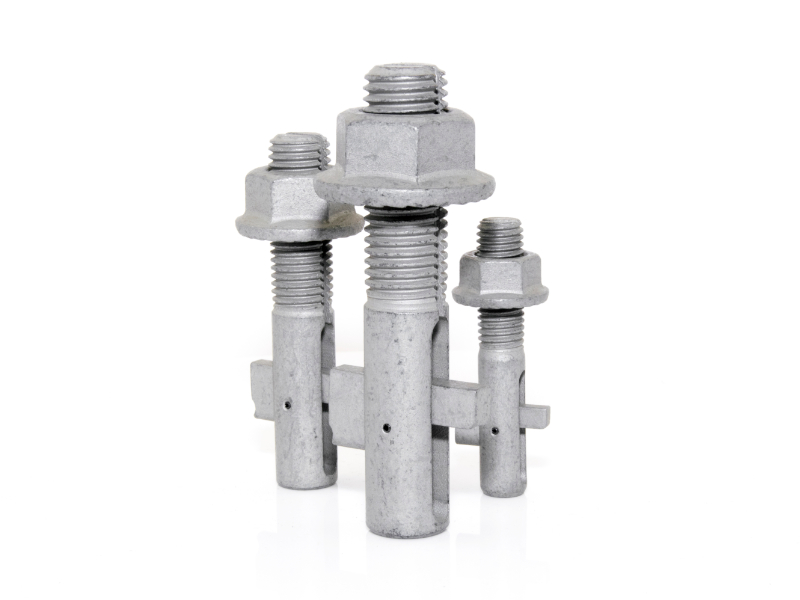
- 2.28Arbor Bolt
- 2.29Blind Bolt
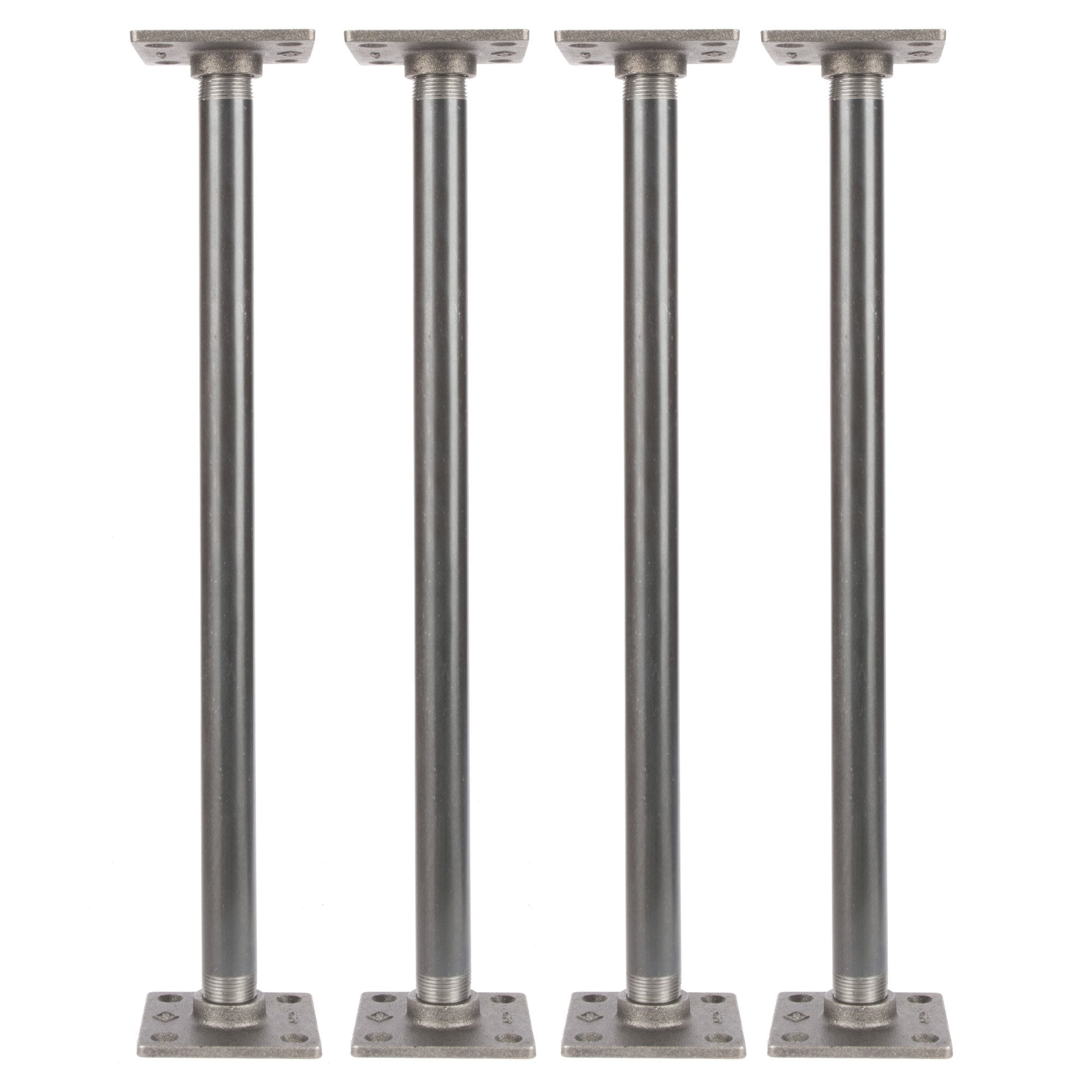
- 2.30Furniture Leg Bolt (Hanger Bolt)
- 3.0Three Quick Tips for Choosing Fasteners
From simple projects like mounting shelves or building a deck to industrial tasks such as securing equipment or assembling steel frameworks, fasteners are essential components for structural integrity. Selecting the wrong fastener can result in loose joints, equipment failure, or safety hazards.
A key distinction in fasteners is the shank profile: tapered vs. non-tapered.
- Tapered-shank fasteners have sharp, self-tapping points and threads that cut directly into wood, particleboard, drywall, or sheet metal, allowing quick installation with minimal pre-drilling.
- Non-tapered shank fasteners feature uniform shanks and optimized threads for high-strength, precision connections in demanding environments, from high-temperature industrial settings to marine applications.
Selecting the right type ensures efficiency, performance, and long-term reliability. Precision manufacturing technologies, such as the Automatic 2-Roll Thread Rolling Machine and the Hydraulic 3-Roll Thread Rolling Machine, further ensure strong and accurate thread profiles.
1.0Tapered-Shank Fasteners: Versatile Self-Tapping Design
Tapered-shank fasteners are highly adaptable and feature self-tapping points for superior holding power. Their sharp cutting points and optimized threads allow direct installation into wood, particleboard, drywall, and light-gauge metals, often without pre-drilling. To ensure consistent thread quality in mass production, manufacturers use advanced equipment like the CNC 3-Die Thread Rolling Machine.
Material-specific variants now cover chipboard, hardwood, and engineered plastics, broadening their applications. Ideal for drywall anchoring, furniture assembly, decking, or lightweight metal mounting, tapered-shank fasteners offer reliability, efficiency, and compatibility, making them essential for both professional contractors and DIY projects.
1.1Chipboard Screw (Particle Board Screw)
Primary Use: Furniture and cabinet assembly in particleboard, where controlled thread engagement prevents material failure under load.
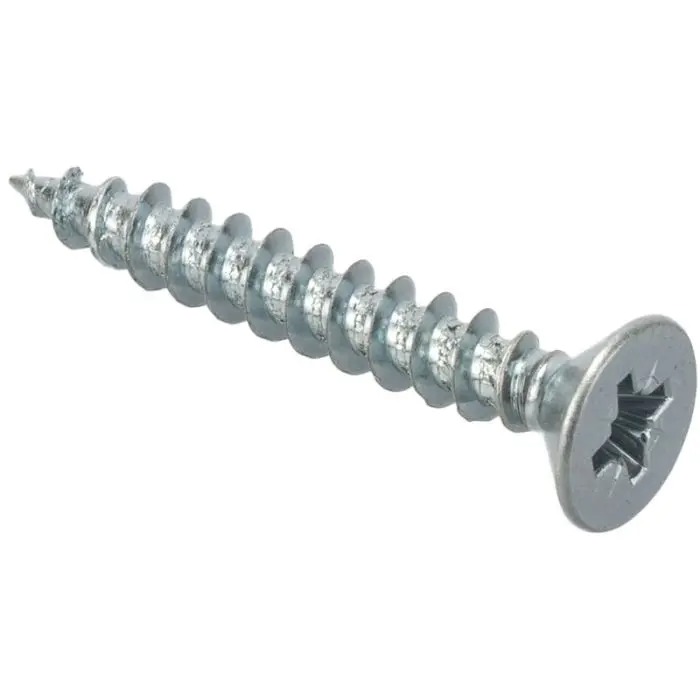

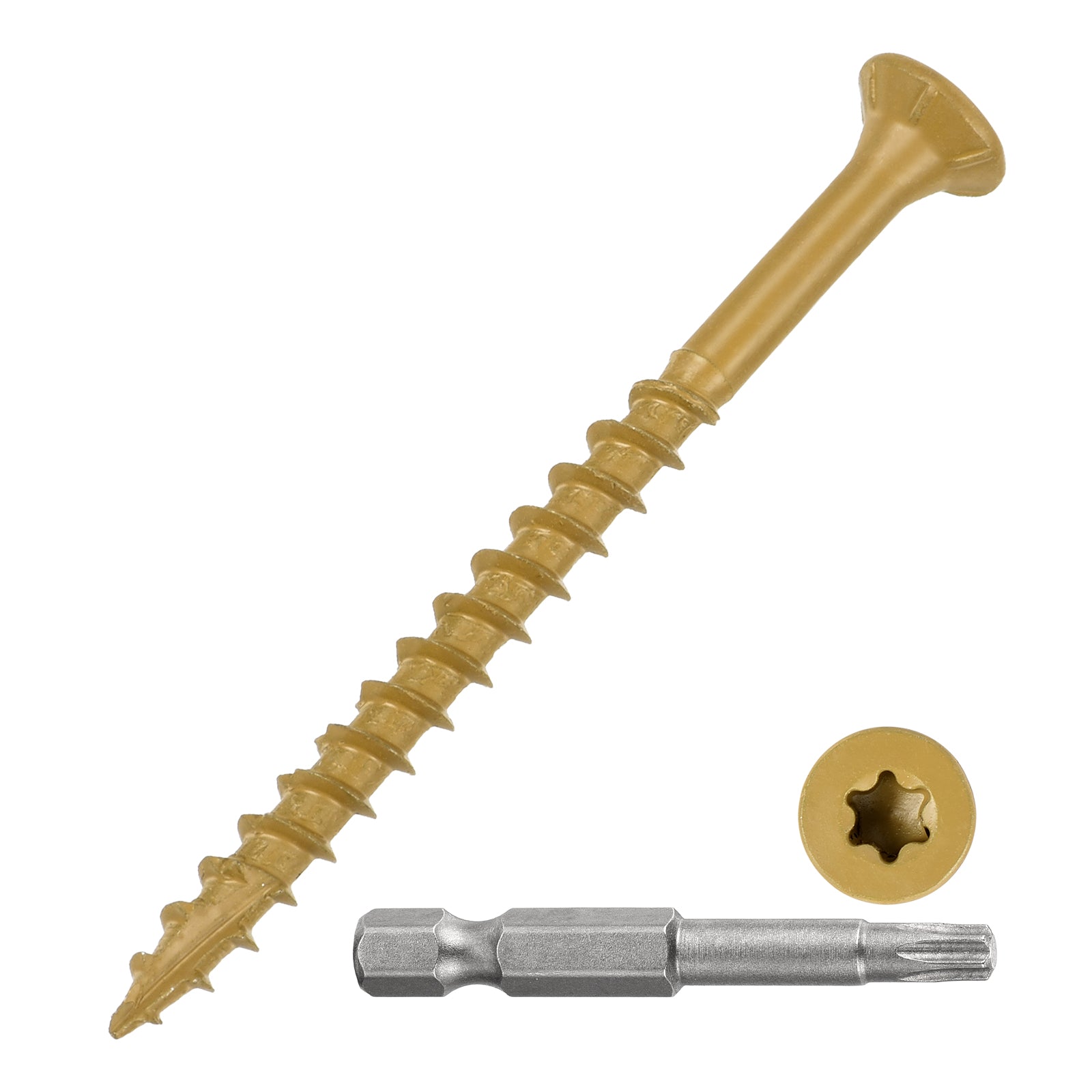
1.2Concrete Screw (Tapcon / Masonry Screw / Confast / Blue Screw / Titen)
Primary Use: Attaching wood, metal, or hardware fixtures (e.g., brackets, hooks, conduits) directly to concrete or brick substrates.
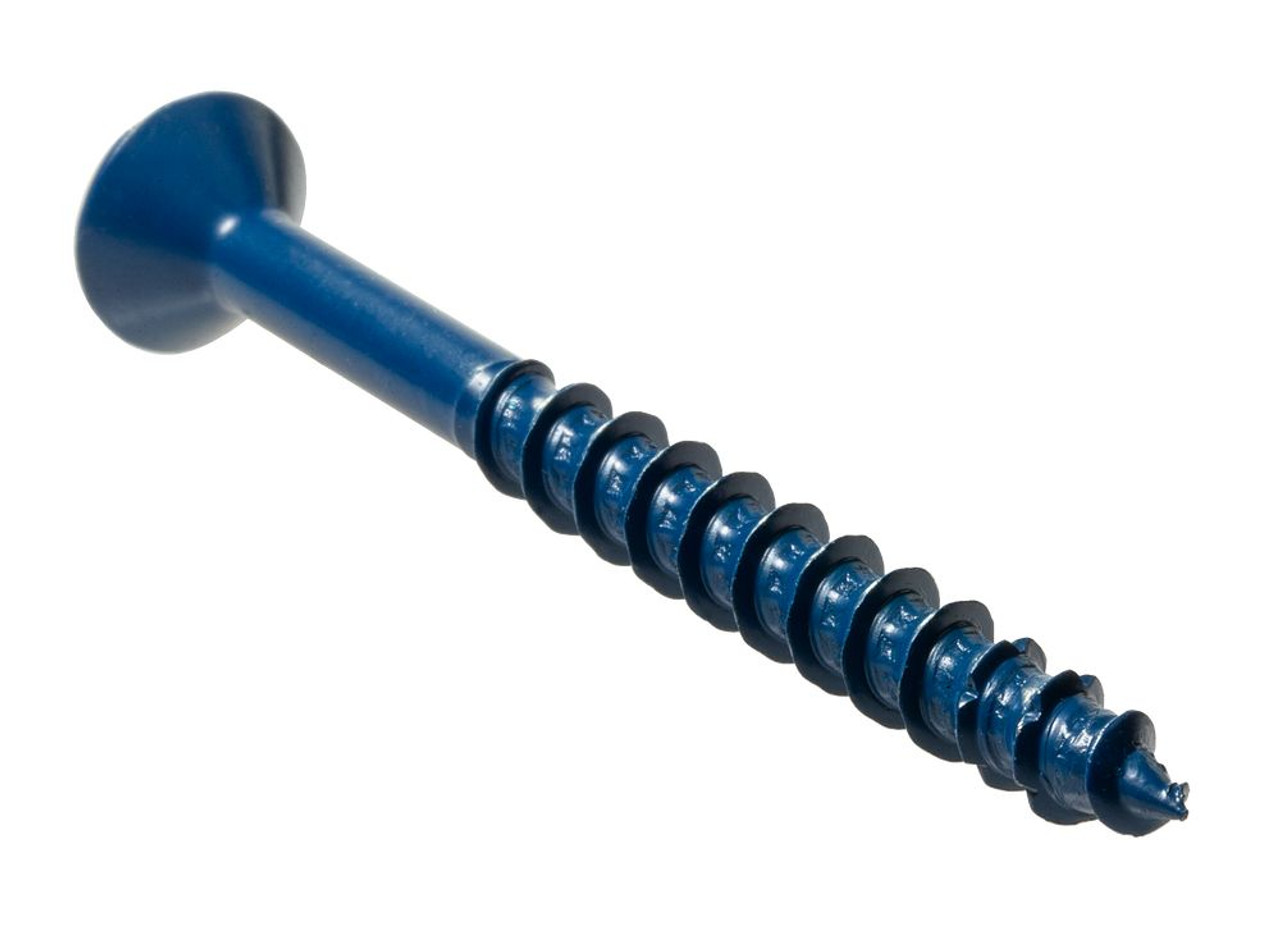

1.3Deck Screw
Primary Use: Outdoor decking, fencing, and structural applications subject to moisture and weathering.

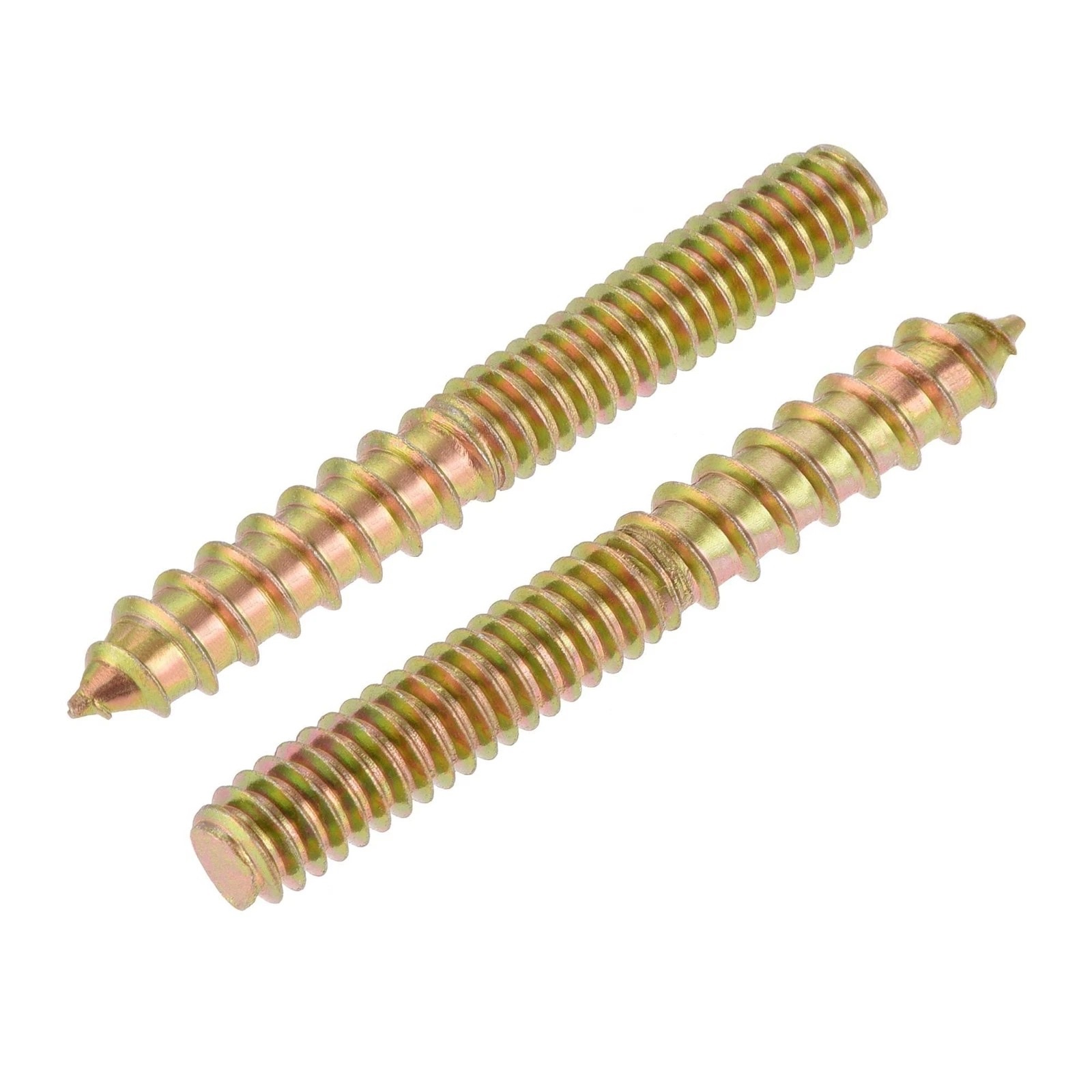
1.4Double-Ended Screw / Hanger Bolt
- Dowel Screw: Headless fasteners with sharp points at both ends, designed for concealed wood-to-wood connections in furniture and panel joints (e.g., table legs).
- Hanger Bolt (Handrail Bolt): Combines a wood screw thread on one end with a machine thread on the other, enabling secure connections between wood members and metal components such as brackets, rails, or fittings.
Primary Use: Structural furniture joints, handrail assemblies, and wood-to-metal connections requiring mechanical strength with minimal visible hardware.

1.5Drive Screw (Hammer Drive Screw)
Primary Use: Permanent attachment of nameplates, identification tags, or rating plates to equipment and machinery.
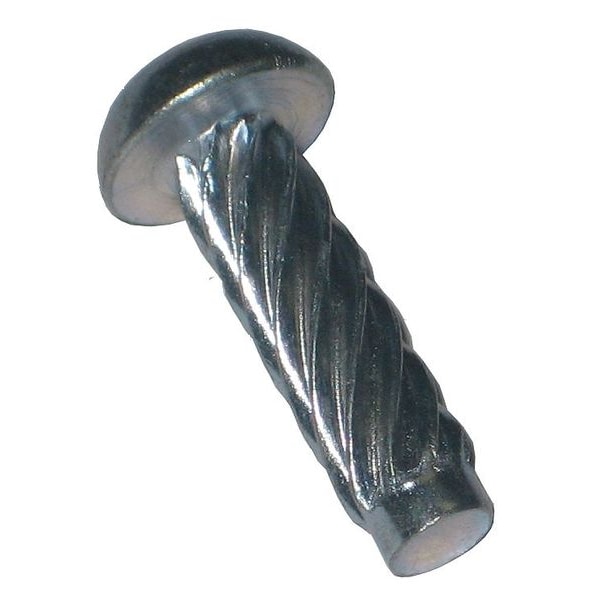

1.6Drywall Screw
Drywall screws are a standard fastener in building construction. Featuring a bugle head that seats flush against drywall, they are designed with a thread diameter larger than the shank to achieve a strong grip in wood or light-gauge steel studs.
Primary Use: Securing drywall sheets to studs; also applied in light wood joinery and basic furniture assembly.

1.7Eye Screw (Screw Eye)
Eye screws are threaded fasteners with a looped head designed for suspension or anchoring.
- Standard Eye Screw: General-purpose type; larger forms (Lag Eye Screws) are used as suspension points for fixtures such as lights, hooks, or hanging planters.
- Vine Eye (UK usage): Features a longer shank with a smaller loop, commonly used to anchor guide wires for climbing plants against walls.
Primary Use: Suspension, hanging fixtures, and anchoring wire or cable systems.
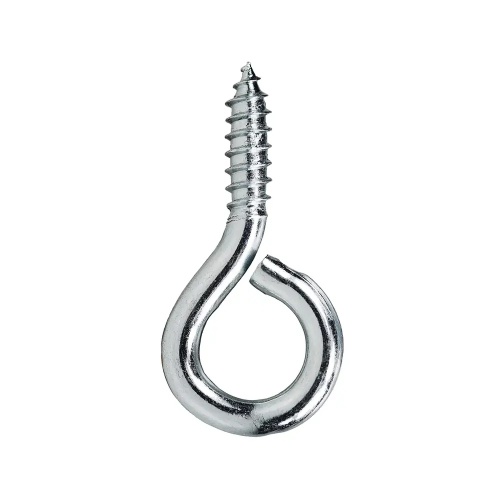

1.8Lag Bolt (Lag Screw / Coach Screw)
Primary Use: Structural timber connections (e.g., beams, bridges, posts) and fastening wood to concrete, such as outdoor columns and heavy frames.
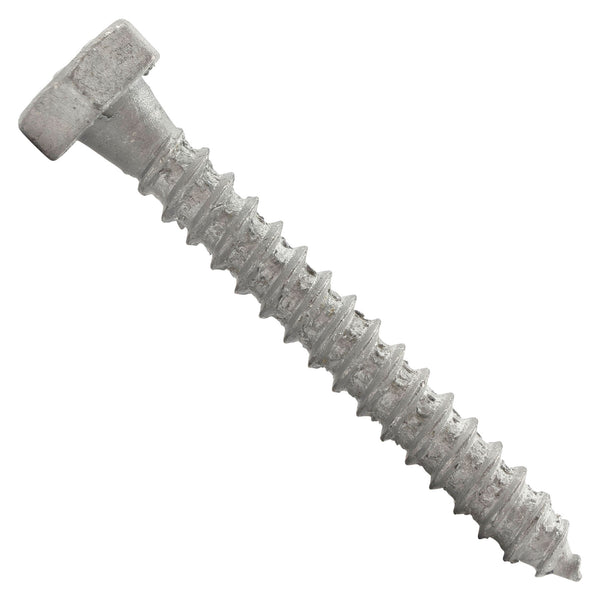

1.9Self-Drilling Wood Screw
Primary Use: Solid wood furniture, outdoor fencing, timber ceiling joists, and other woodworking requiring fast installation.

1.10MDF Screw
Primary Use: Assembly of MDF-based furniture, decorative panels, shelving, and custom cabinetry.

1.11Plastic Self-Tapping Screw
Primary Use: PVC pipe fittings, plastic housings in electronics, and fastening components in appliances or lightweight plastic assemblies.

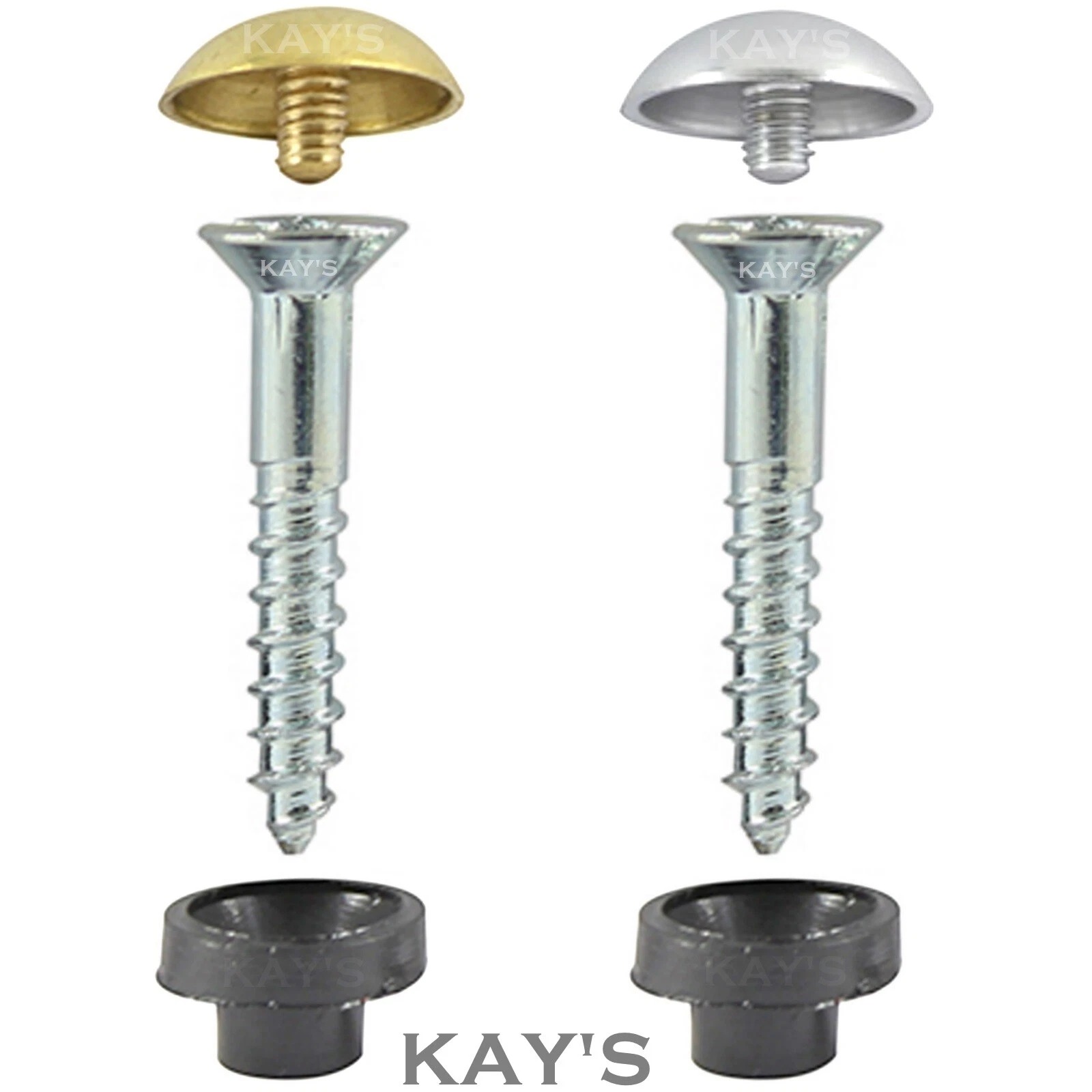
1.12Mirror Screw
- Description: Flat-head screw with a central threaded hole that accepts a decorative chrome-plated cover cap, combining mechanical strength with a clean, finished appearance.
- Primary Use: Mounting mirrors, panels, or fixtures where aesthetics and flush finishing are critical.

1.13Sheet Metal Screw
- Description: Fully threaded screw with sharp points to penetrate and secure thin-gauge metal, plastic, or wood sheets. Some variants include chip-clearance slots for easier installation.
- Primary Use: Fastening sheet metal assemblies, HVAC ductwork, enclosures, and lightweight structural connections.

1.14Twinfast Screw
- Description: Screw with dual thread starts, allowing approximately twice the driving speed compared to conventional single-thread screws.
- Primary Use: Rapid installation in drywall, light framing, and panel fastening.

1.15Wood Screw
- Description: Traditional wood-to-wood fastener, typically partially threaded to draw members tightly together. Available in multiple head styles (flat, oval, pan) and standardized under ANSI B18.6.1 and DIN 95/96/97.
- Primary Use: General woodworking, furniture assembly, and carpentry across a wide range of applications.

1.16Security Head Screw
- Description: Screw with specialized drive profiles (tri-wing, hex-pin, breakaway), requiring dedicated tools for removal and providing tamper resistance. Made in stainless steel and alloy steel variants.
- Primary Use: Public infrastructure (streetlights, traffic signs), safety enclosures, and applications requiring vandalism or theft protection.

2.0Non-Tapered Shank Fasteners: Precision & Heavy-Duty Applications
Non-tapered fasteners are designed for high-performance applications. They use continuous threading, locking features, and high-grade materials to handle extreme loads and maintain precise alignment in harsh conditions like high temperatures, marine environments, and vibration.
Advanced manufacturing with the Automatic CNC Screw Thread Rolling Machine ensures uniform, reliable threads for critical structural use. Typical applications include structural anchors, industrial machinery assemblies, offshore platforms, and high-pressure systems. These fasteners deliver strength, precision, and durability where reliability is essential.
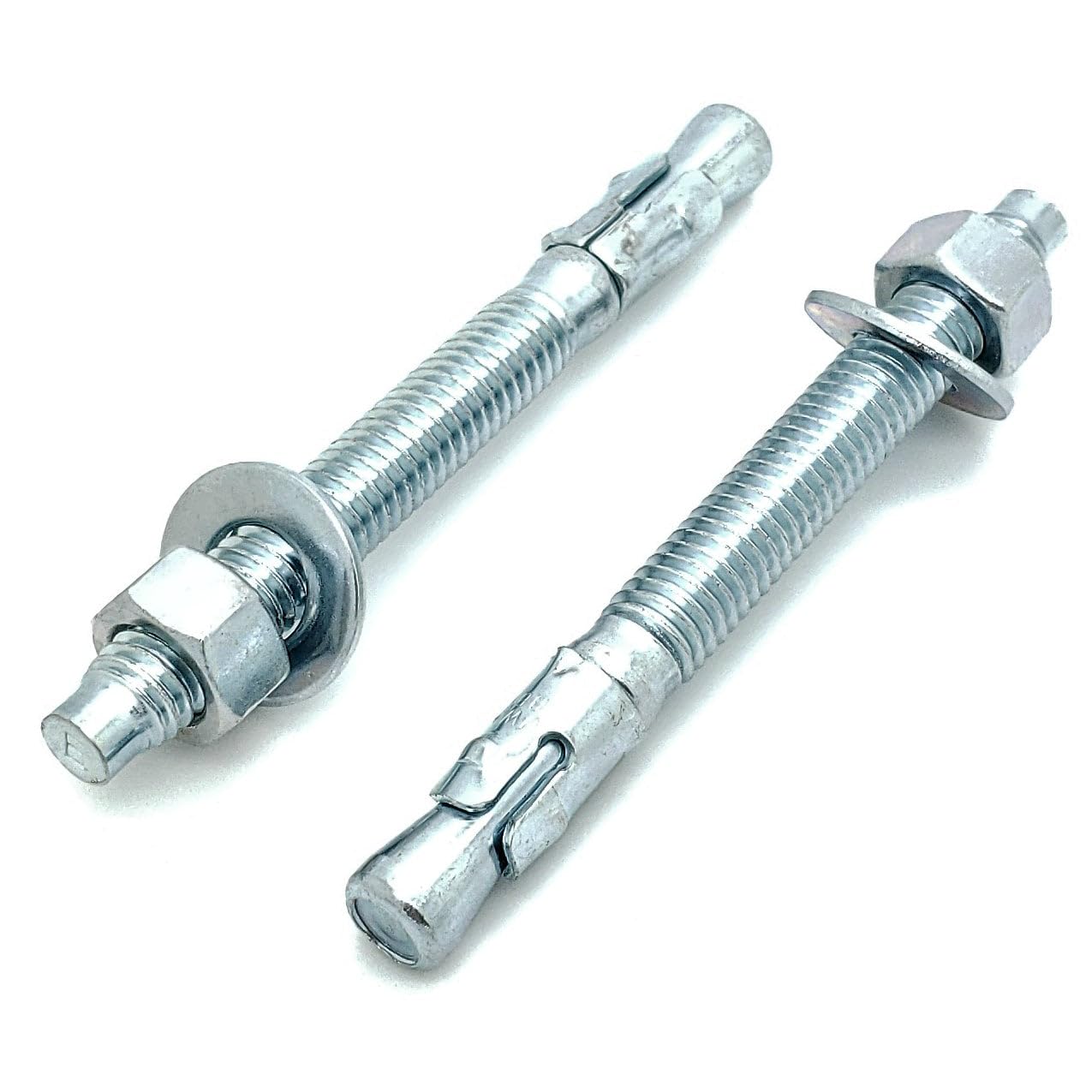
2.1Anchor Bolt
Anchor bolts are embedded in concrete, leaving the threaded portion exposed to accommodate nut fastening. Designed to transfer both tensile and shear loads, they provide secure anchorage between structural or mechanical elements and concrete substrates.
Primary Use: Fixing steel columns to foundations, securing façade systems, or fastening equipment brackets and machinery bases to concrete walls and floors.

2.2Breakaway Bolt
Breakaway bolts feature a hollow or engineered shank designed to fracture under controlled impact or overload conditions. This intentional failure mechanism prevents damage to primary structures. In aerospace applications, hollow shank construction also offers weight reduction.
Primary Use: Fire hydrants and fire protection systems (preventing structural damage during collisions), as well as aerospace assemblies requiring controlled breakage or weight optimization.

2.3Cap Screw
A general classification that encompasses a wide range of head styles, including hex, flat, round, and socket heads. Defined under ASME B18.6.2 and ASME B18.3, cap screws are typically used without nuts, threading directly into tapped holes.
Primary Use: Engines, machinery, and precision equipment where fastener head geometry must match assembly requirements.

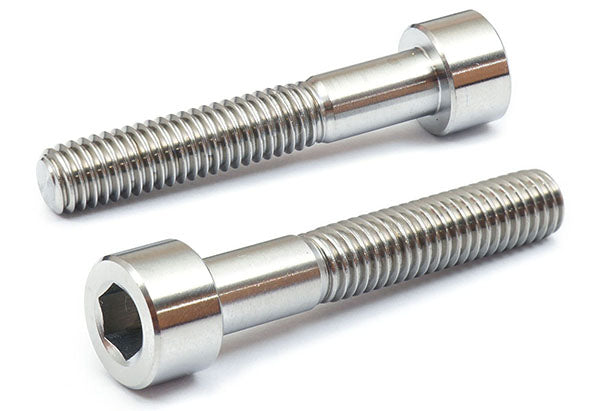
2.4Socket Screw (Allen Bolt / Socket Head Cap Screw)
Socket screws incorporate a cylindrical head with an internal hex drive, requiring an Allen key or hex wrench for installation. Their compact head profile enables use in confined spaces, while high-strength alloy steel variants maintain structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 587 °C.
Primary Use: Engines, electronic devices, furniture, and assemblies requiring a flush, unobtrusive finish with high mechanical performance.

2.5Carriage Bolt (Cup Head Bolt / Coach Bolt)
Carriage bolts are characterized by a domed or countersunk head with a square or ribbed neck directly beneath. This design locks the bolt in place during tightening, allowing installation from one side only and leaving a smooth, tamper-resistant head on the exposed surface.
Primary Use: Fencing, wooden gates, vehicle structures, and applications requiring single-sided installation with enhanced safety or vandal resistance.

2.6High-Temperature & High-Pressure Bolt
Specialized bolts designed for extreme service conditions such as boilers, steam pipelines, and nuclear or chemical reactors operating above 300 °C and 10 MPa.
- Materials: Nickel-based alloys (e.g., Inconel 718) or high-temperature stainless steels (e.g., 310S).
- Structure: Often incorporates gasket grooves to accommodate metal or graphite seals.
- Threads: Fine-pitch profiles provide precise preload control and minimize relaxation at elevated temperatures.
Primary Use: Power plant boilers, chemical processing reactors, and nuclear steam generator assemblies.

2.7Micro Precision Screw
Primary Use: Electronics (smartphones, wearables), medical instruments, microsensors, and precision optical devices.

2.8Anti-Vibration Locking Bolt
Bolts are designed for high-vibration environments such as automotive, rail, and rotating machinery.
- Locking Methods: Nylon insert locking, dual-thread configurations, or serrated-head interfaces to resist loosening under vibration.
- Materials: High-strength steels (Grade 8.8 or higher), typically with anti-corrosion coatings.
Primary Use: Automotive engines, rail axles, electric motor housings, and pump flanges where vibration resistance is critical.

2.9Marine-Grade Bolt
Fasteners engineered for long-term performance in marine and offshore environments with high saltwater exposure.
- Materials: Super duplex stainless steels (e.g., 2507) or titanium alloys for superior corrosion resistance.
- Coatings: Fluoropolymer or ceramic coatings capable of exceeding 1000 hours in salt spray testing.
- Design: Sloped head geometries and drainage features to prevent water entrapment.
Primary Use: Ship decks, offshore oil and gas platforms, port infrastructure, and desalination facilities.
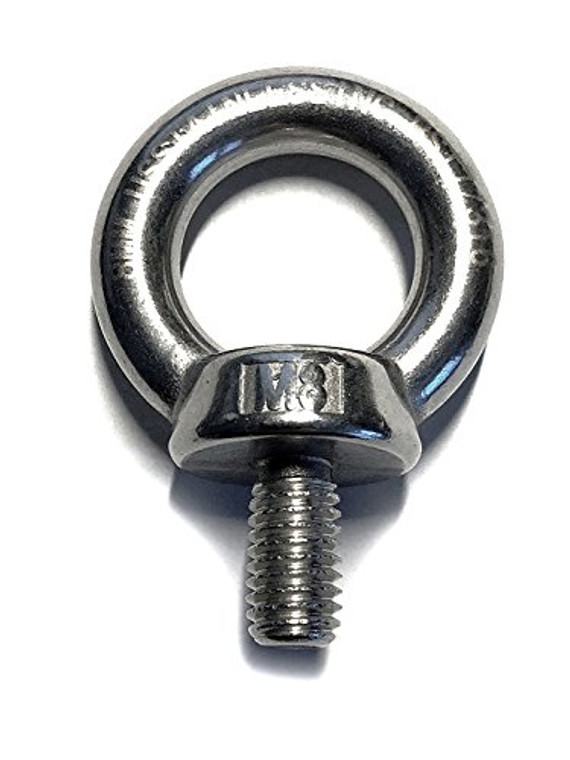

2.10Confirmat Screw
Designed for particleboard and MDF, with a large thread diameter that provides higher pull-out resistance than standard wood screws.
Primary Use: Cabinet and furniture assembly in engineered wood products.
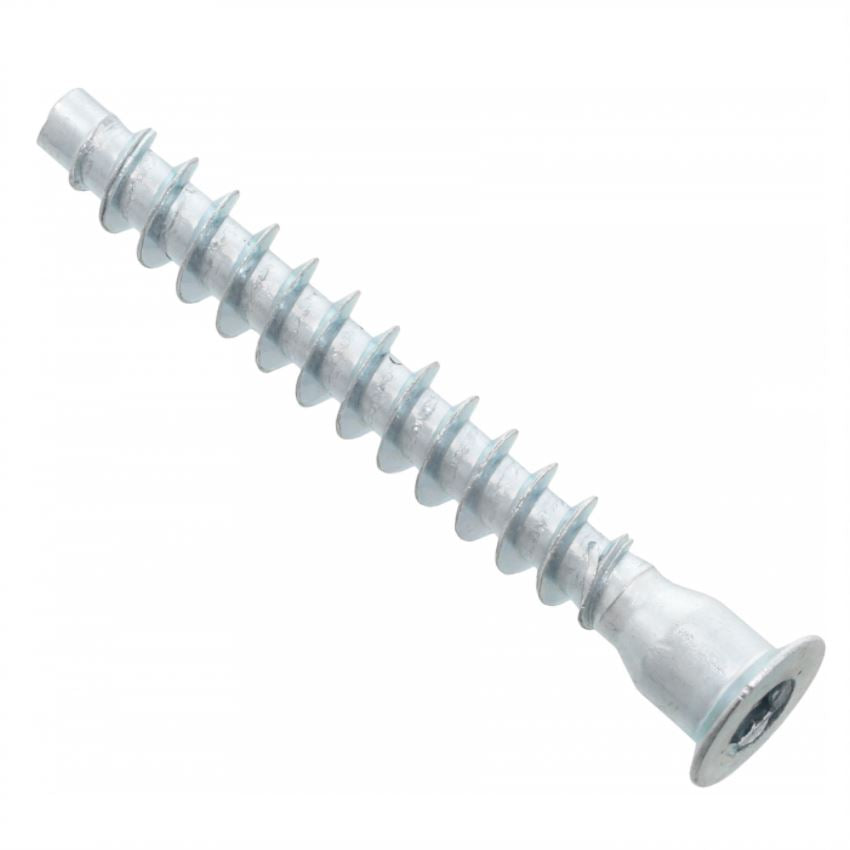

2.11Elevator Bolt
Primary Use: Conveyor belts, elevators, and adjustable furniture where a flush surface is required.
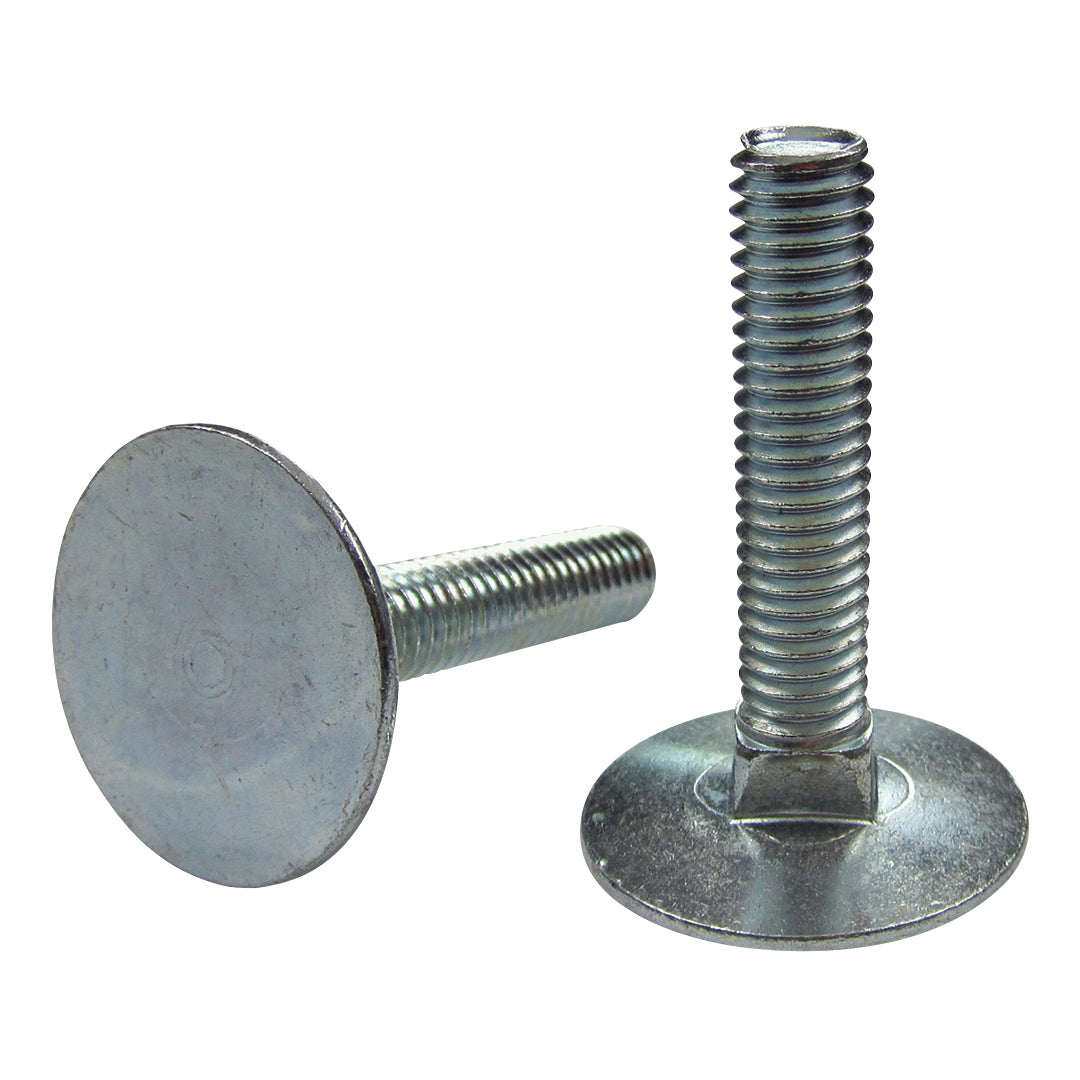

2.12Eye Bolt
Primary Use: Lifting points, cable terminations, and suspension systems.
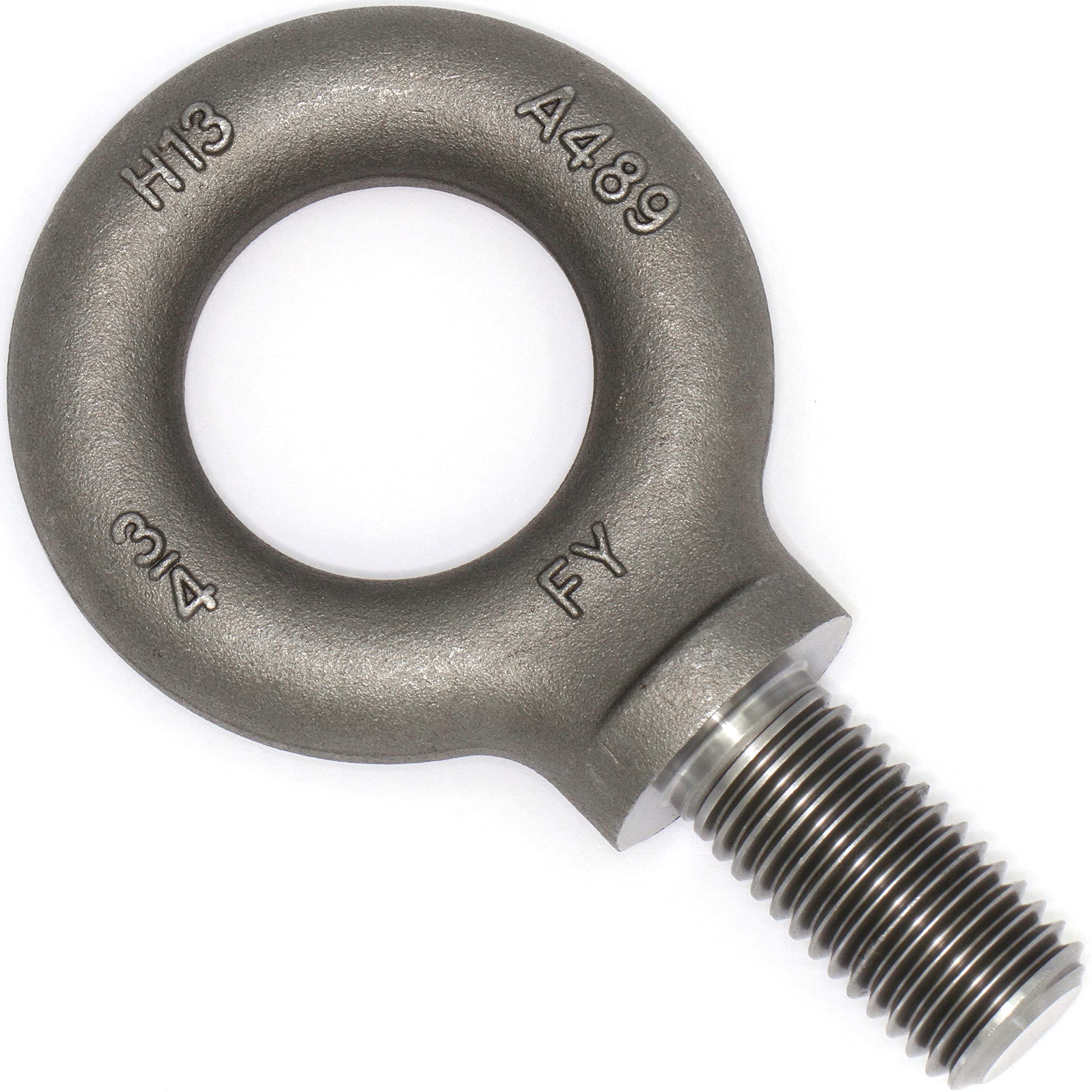

2.13Hex Cap Screw
Primary Use: High-strength machinery, automotive, and structural assemblies requiring precision.

2.14Fine Adjustment Screw
Primary Use: Precision instruments such as microscopes, optical devices, and calibration equipment.

2.15Machine Screw
Primary Use: Mechanical and electronic assemblies, panels, and metal-to-metal fastening.

2.16Stove Bolt (Gutter Bolt)
Primary Use: Sheet-metal assemblies, ductwork, and general light-duty fastening.

2.17Plow Bolt
Primary Use: Heavy earth-moving equipment, grader blades, and plows.
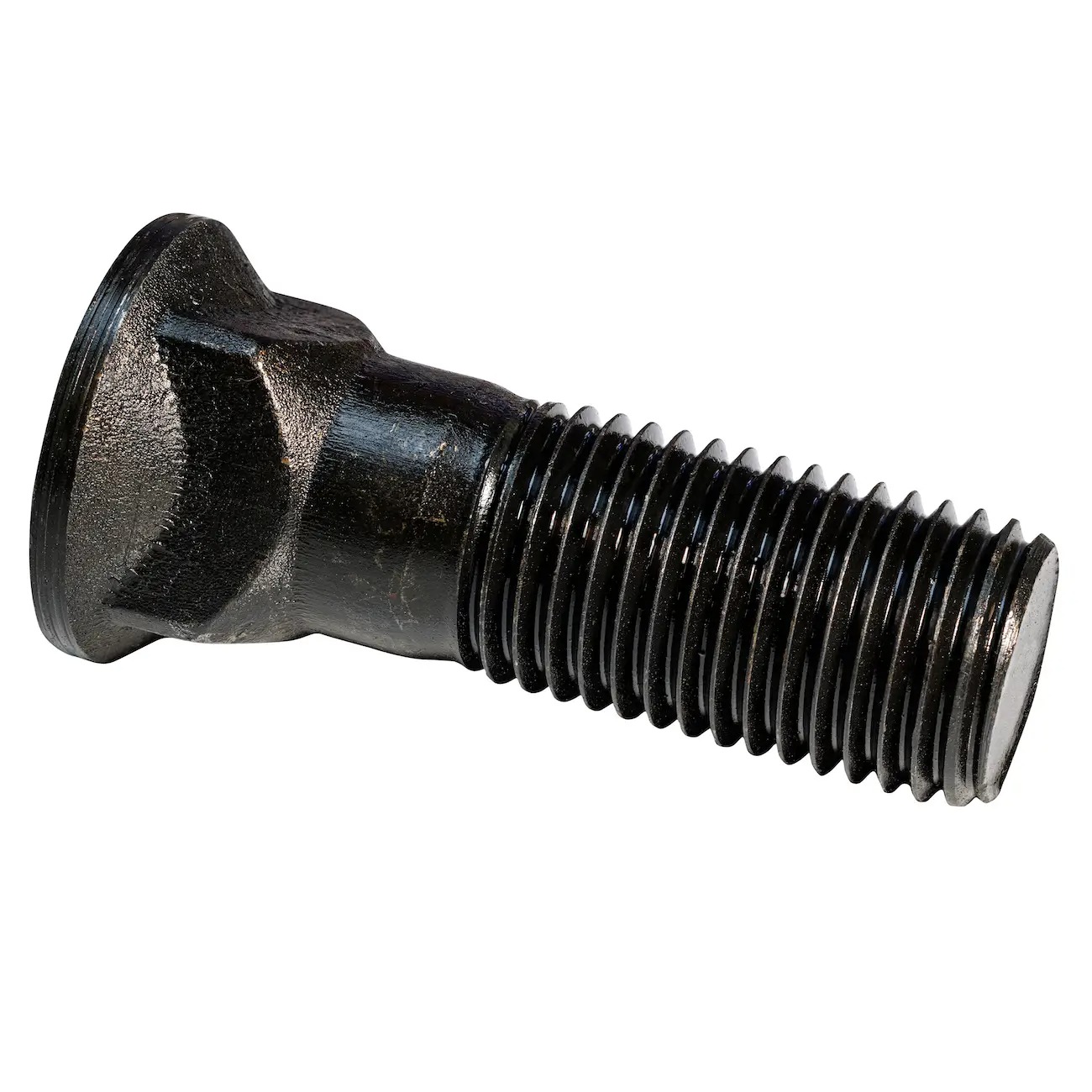

2.18Self-Drilling Screw (Tek Screw)
Primary Use: Steel framing, roofing sheets, and structural metal-to-metal connections.
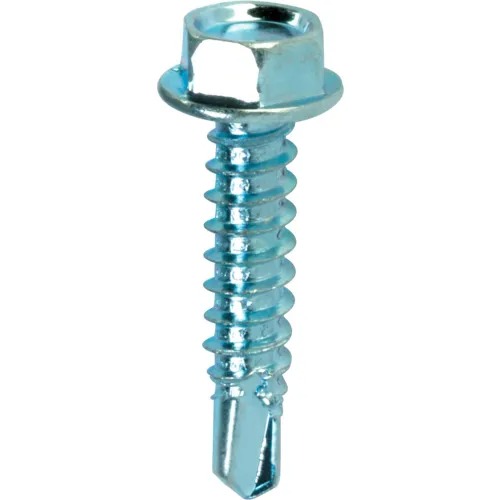

2.19Self-Tapping Machine Screw
Primary Use: Sheet-metal housings, electronics, and serviceable enclosures.
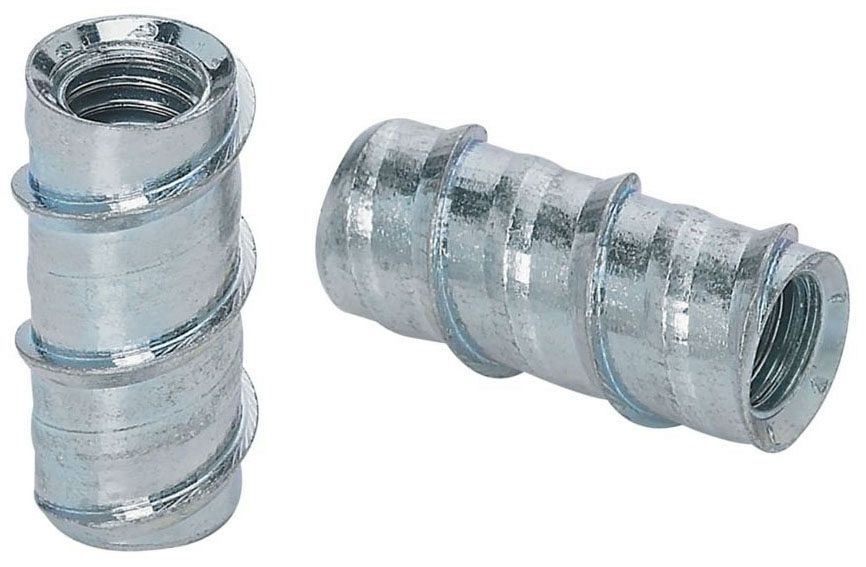

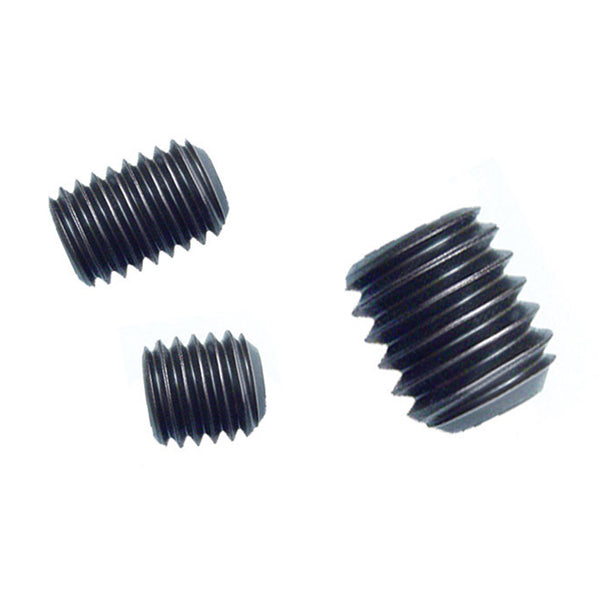
2.20Set Screw (Grub Screw)
Headless or low-profile screw used to secure rotating parts onto shafts.
Primary Use: Gear hubs, pulleys, collars, and rotating machinery components.

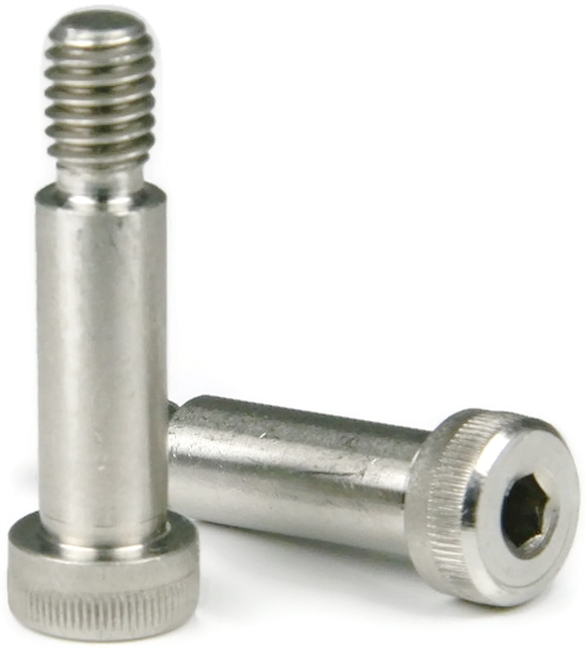
2.21Shoulder Bolt (Stripper Bolt)
Primary Use: Mold tooling, linkages, and mechanisms requiring controlled sliding or rotation.

2.22Tension Control (TC) Bolt
Primary Use: Steel framework connections in bridges, buildings, and heavy structures.
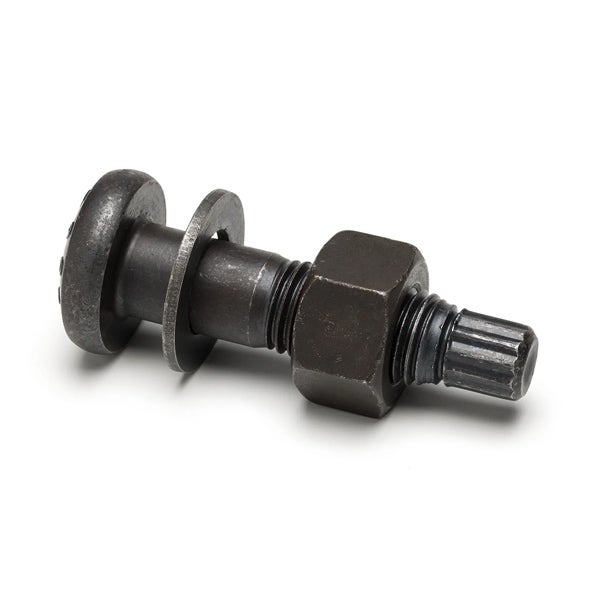

2.23Thread Rolling Screw
Primary Use: Electronics, appliances, and food-processing equipment.

2.24Sex Bolt (Chicago Screw)
Primary Use: Furniture, binders, architectural signage, and bookbinding.

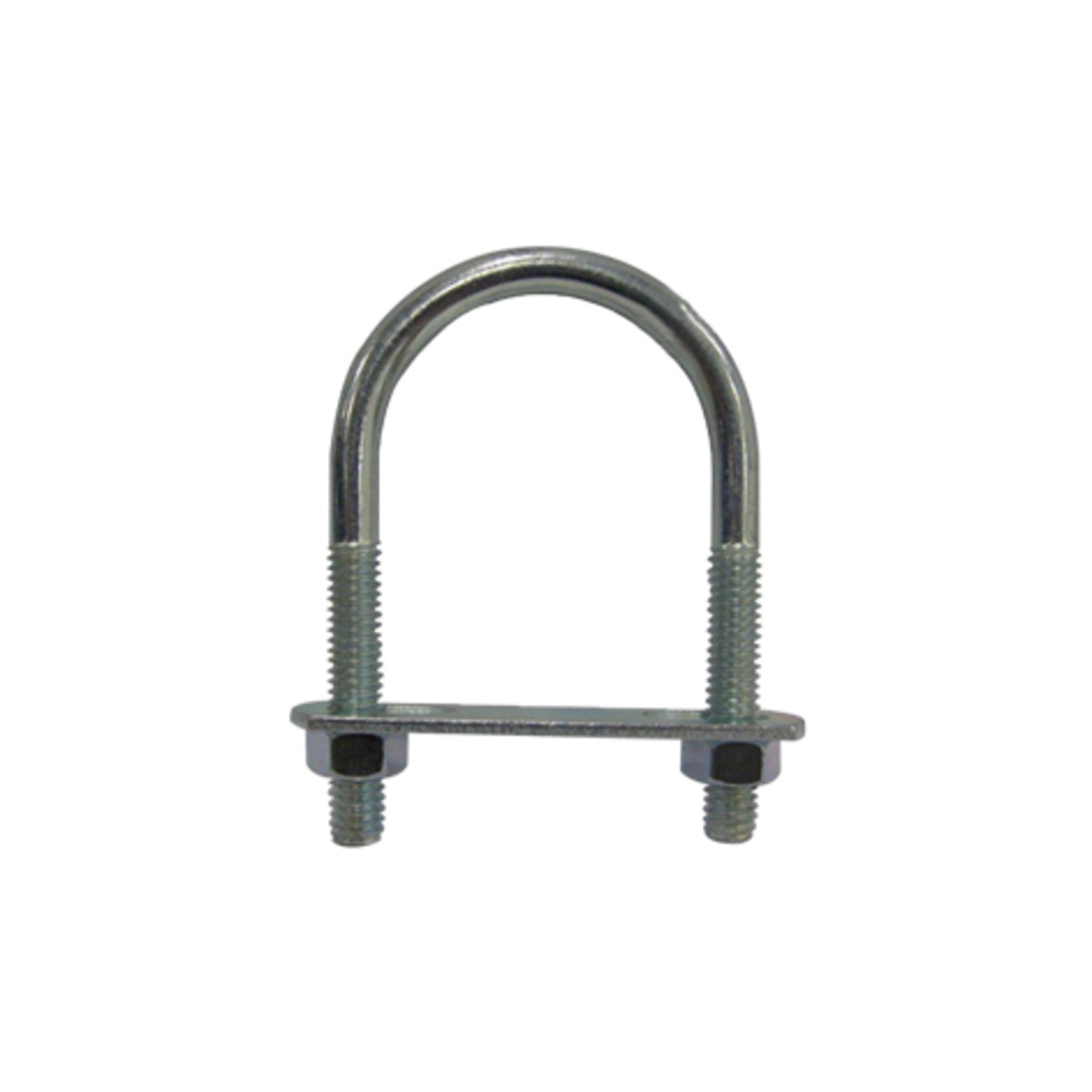
2.25U-Bolt / J-Bolt
- U-Bolt: U-shaped with two threaded ends for pipe or conduit clamping.
- J-Bolt: J-shaped, embedded into concrete as a structural anchor.
Primary Use: Pipe support systems, pole anchoring, and embedded connections.

2.26Hook Bolt
Primary Use: Hanging loads, piping, and industrial supports.

2.27Expansion Bolt (Dynabolt)
Primary Use: Heavy-duty anchoring in concrete structures, machinery bases, and supports.

2.28Arbor Bolt
Primary Use: Circular saws, grinders, and rotating blade equipment.
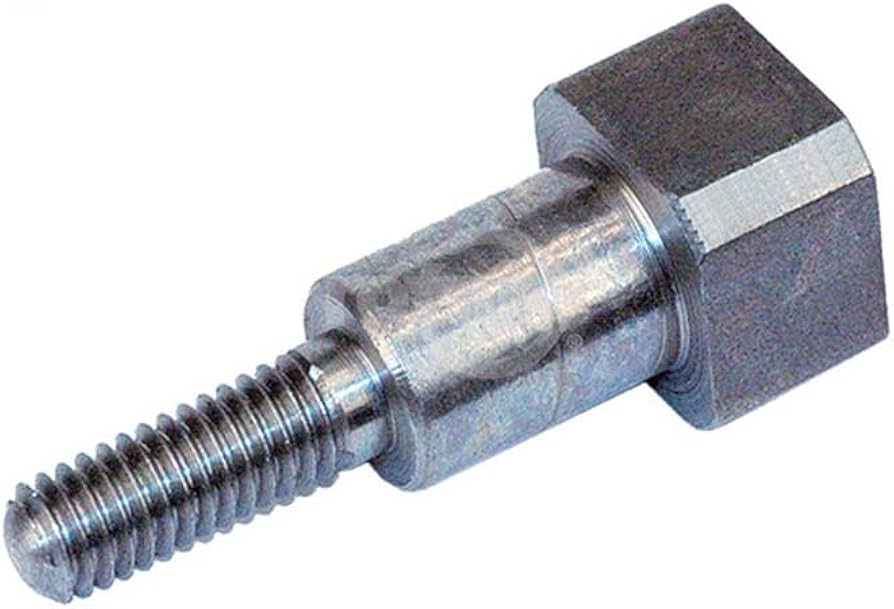
2.29Blind Bolt
Primary Use: Steel structures, hollow sections, and pipeline walls.

2.30Furniture Leg Bolt (Hanger Bolt)
Primary Use: Furniture assembly, particularly detachable leg connections.

3.0Three Quick Tips for Choosing Fasteners
Consider the material: Wood → wood screws or lag bolts; Concrete → concrete screws or anchor bolts; Outdoor → stainless steel for corrosion resistance.
Consider the load: Heavy-duty structural connections → TC bolts or lag bolts; Fine adjustments → fine-thread screws.
Consider installation access: One-sided installation → carriage bolts; Tight spaces → socket (Allen) bolts; Hidden hardware → sex bolts or dowel screws.







